To help determine what you’re experiencing, focus on how the pain feels, the location of the pain, when it started and how long it lasts
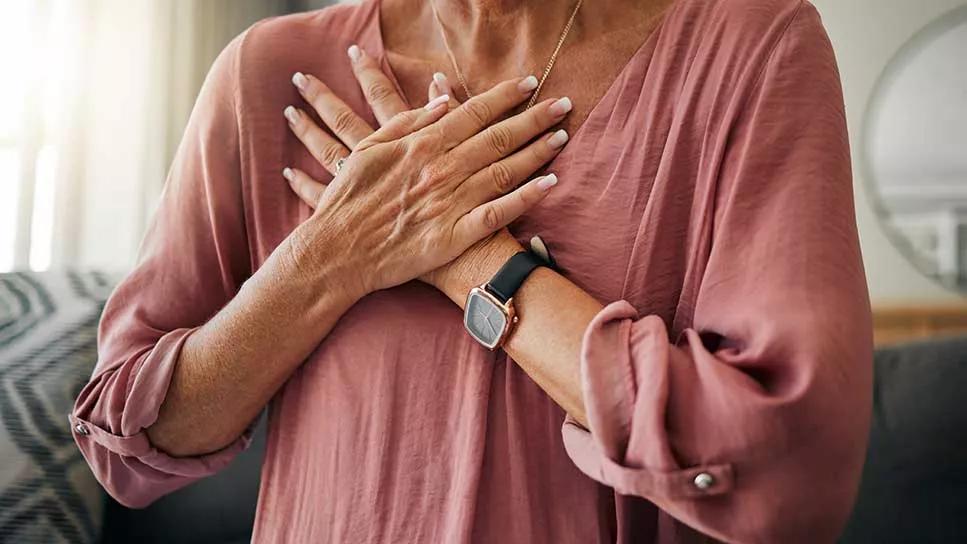

The symptoms come on quickly: You feel your chest tighten, your heart rate skyrockets and you start sweating.
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
It’s an alarming scenario, and your mind races to figure out what’s happening. Is it a heart attack? Or is it a panic attack? It can often be difficult to tell the difference (especially if you’ve had neither) and that only adds to the confusion and stress.
Both events are serious and it’s important to recognize which one you’re experiencing so you can get proper treatment.
So, how can you tell the difference when it comes to a panic attack vs. a heart attack? You want to focus on how the pain feels, the location of your pain, when it started and how long it lasts.
Cardiologist Mistyann-Blue Miller, MD, explains what these two conditions have in common and how they’re different.
A heart attack is when part of your heart doesn’t get enough blood. This usually happens because an artery that supplies blood to your heart is blocked.
A panic attack is a sudden attack of overwhelming fear or anxiety, triggered by your body’s fight-or-flight response. Panic attacks aren’t life-threatening, but they interfere with your quality of life and mental well-being.
People who have regular or frequent panic attacks may have a panic disorder, a type of anxiety disorder. But an isolated panic attack can happen to anyone, even without a panic disorder diagnosis.
While it’s easy to confuse both conditions and how they feel, you want to really focus on how your chest pain feels.
First, let’s talk about the symptoms associated with both conditions.
Common heart attack symptoms include:
Remember, a heart attack can be life-threatening, so don’t wait to see if the symptoms go away. Seek immediate medical care if you have signs of a heart attack.
Symptoms of a panic attack include:
In many cases, a panic attack triggers a fast heart rate, also known as tachycardia. The heart rate may speed up to 200 beats per minute or even faster.
A fast heart rate can make you feel lightheaded and short of breath. Or you might feel fluttering or pounding in your chest. Usually, tachycardia that happens in response to emotional stress and only lasts a few minutes isn’t harmful. But if it happens regularly, or you have possible symptoms of a heart attack, seek medical care.
So, while some symptoms of a heart attack vs. a panic attack overlap, like chest pain, shortness of breath, nausea and feelings of impending doom, Dr. Miller explains the key distinctions to watch for.
While both heart and panic attacks cause chest discomfort, you want to zero in on where the pain is.
“With a heart attack, pain radiates to other areas like the arm, jaw or neck,” says Dr. Miller. “If it’s a panic attack, pain will typically stay in the chest.”
Another key difference between a heart attack and a panic attack? Heart attacks tend to happen after physical strain or exertion — a sign not found in panic attacks.
“A heart attack might happen after shoveling snow or walking up a long flight of stairs,” clarifies Dr. Miller. “But you wouldn’t have a panic attack after exercise unless there was an emotional stress trigger with it.”
But what if the symptoms hit you at night? Both panic attacks and heart attacks can wake you from sleep. But there’s a key difference: People who have nighttime, or nocturnal, panic attacks usually have daytime panic attacks, too.
So, if you wake up with chest pain or other symptoms, and you don’t have a history of panic attacks, that might be a sign of a heart attack.
Panic attack symptoms last a few minutes or up to an hour. Then, the symptoms disappear, and you feel better. But a heart attack won’t let up.
Pain and symptoms of a heart attack might keep going or come in waves where it gets better and worse.
“Heart attacks can cause severe chest pain, like a 9 or 10 on the pain scale,” states Dr. Miller. “Then later, the pain may drop to a 3 or 4 before it gets worse again. The pain might change, but it won’t go away.”
One thing of note? Emotional stress plays a role in both conditions.
“Both panic attacks and heart attacks can occur during or after a stressful situation,” says Dr. Miller. “But most of the time, people have a panic attack rather than a heart attack in response to emotional stress.”
People who have anxiety, depression or chronic stress may have a higher risk of heart problems. Chronic stress can lead to high blood pressure, which raises the risk of heart attack and stroke.
It’s also important to know that a heart attack might seem like it came out of nowhere. But in many cases, chest pain due to heart disease, known as angina, appears in the days or weeks before a cardiac event.
“You may feel a twinge or some pain in the shoulder or chest but think it’s something else,” notes Dr. Miller. “The symptoms go away. Then later, the pain gets worse, or you feel a little off. Then, the heart attack hits. These early signs can be hard to identify.”
A heart attack is a medical emergency. A panic attack isn’t. But with the overlap in symptoms, it can be tough to tell them apart. Don’t take chances. If you have chest pain or other heart attack symptoms — or if you’re not sure if it’s a heart attack or panic attack — seek immediate medical care.
Learn more about our editorial process.

Absolutely! In fact, in many ways, exercise is key to recovery

There’s no way to stop it once a heart attack is happening, but the most important thing you can do is to call for help

You can counter the risk of prediabetes-related heart attack or stroke by eating more fruits, vegetables and whole grains, as well as exercising regularly

An ideal blood pressure is less than 120 mm Hg systolic and less than 80 mm Hg diastolic
Your natural estrogen levels support a healthy heart by improving your cholesterol, increasing blood flow and reducing free radicals

Stopping this critical medication on your own increases the risk of heart attack, stroke and more

The emotional toll of loss and other strong emotions can have life-threatening physical effects

Don’t ignore chest pressure that lingers and can’t be explained

Your metabolism may torch 1,300 to 2,000 calories daily with no activity

A gentle touch in all the right places may help drain your sinuses