A PSA (prostate-specific antigen) test is a blood test that helps healthcare providers diagnose and manage prostate cancer. High PSA levels don’t mean you have prostate cancer. But you’re at a higher risk. You may need additional testing and observation to make sure.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Advertisement
Advertisement
Advertisement
Advertisement
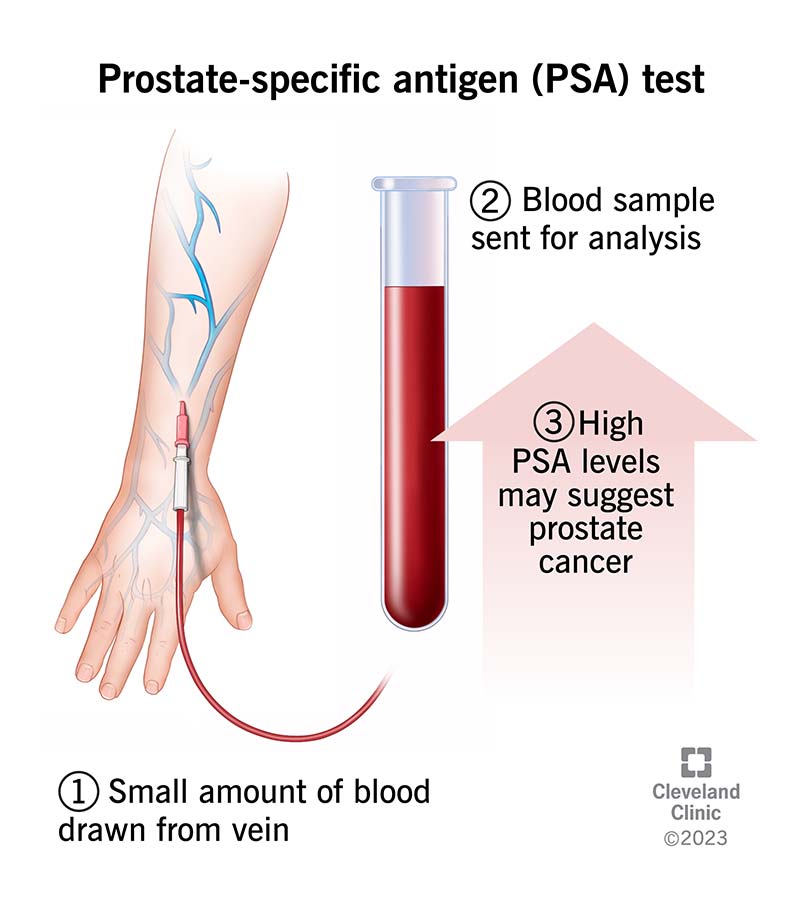
A prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test measures the amount of PSA in your body. It’s a type of blood test that reveals if you have elevated PSA levels. PSA is a protein that your prostate gland makes. Normal and cancerous prostate tissue make PSA. But prostate cancer tends to produce PSA in higher amounts.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Healthcare providers recommend PSA tests for males to screen for prostate cancer. Catching prostate cancer early with a PSA test increases your chances of effective treatment.
A provider will usually conduct a digital rectal exam (DRE) along with a PSA test.
A normal PSA depends on your age. Your PSA levels slowly increase as you get older, even if you don’t have prostate cancer or any other conditions that affect your prostate. Elevated PSA levels may indicate that you have prostate cancer.
Healthcare providers measure PSA in your blood in nanograms per milliliter of blood (ng/ml).
| Age | Normal Level (ng/ml) | Abnormal Level (ng/ml) |
|---|---|---|
| 40 to 50 | 0 to 2.5 | Higher than 2.5 |
| 50 to 60 | 2.5 to 3.5 | Higher than 3.5 |
| 60 to 70 | 3.5 to 4.5 | Higher than 4.5 |
| 70 to 80 | 4.5 to 5.5 | Higher than 5.5 |
| Age | ||
| 40 to 50 | ||
| Normal Level (ng/ml) | ||
| 0 to 2.5 | ||
| Abnormal Level (ng/ml) | ||
| Higher than 2.5 | ||
| 50 to 60 | ||
| Normal Level (ng/ml) | ||
| 2.5 to 3.5 | ||
| Abnormal Level (ng/ml) | ||
| Higher than 3.5 | ||
| 60 to 70 | ||
| Normal Level (ng/ml) | ||
| 3.5 to 4.5 | ||
| Abnormal Level (ng/ml) | ||
| Higher than 4.5 | ||
| 70 to 80 | ||
| Normal Level (ng/ml) | ||
| 4.5 to 5.5 | ||
| Abnormal Level (ng/ml) | ||
| Higher than 5.5 |
PSA tests are very common. If you have a prostate, most healthcare providers recommend getting a PSA test every two to three years, starting around age 50.
If your PSA test results are abnormal, a provider may recommend close observation, with PSA tests and other screenings every six to 12 months.
If you have a high risk of prostate cancer, a provider may recommend getting regular PSA tests starting around 40. You may have a high risk of prostate cancer if you:
Advertisement
If you have prostate cancer, a provider may also recommend a PSA test to assess the effectiveness of your treatment or to make sure prostate cancer hasn’t come back.
Before a PSA test, tell a healthcare provider if you:
These medications and procedures can affect your PSA levels, which prevents a provider from getting an accurate reading.
A provider will give you directions a few days before your PSA test to help ensure you get the most accurate reading. These include:
A PSA test is a type of blood test. During a PSA blood test, a healthcare provider will:
The blood draw for a PSA test usually takes only a few minutes. A healthcare provider may recommend resting for another few minutes before standing up and leaving.
After the healthcare provider removes the needle, they’ll put clean cotton or gauze on the puncture wound and apply pressure to help stop any bleeding. They’ll then place a bandage on your skin.
Keep the bandage on for a few hours and keep it dry. You should also drink plenty of fluids and avoid exercising for a few hours after your blood test. Exercising after a blood draw puts you at an increased risk of:
Risks or complications of a PSA test include:
Advertisement
PSA levels vary in range according to your age. If your PSA levels are higher than expected for your age range, it doesn’t mean that you have prostate cancer. But you might have a higher risk. Healthcare providers will order additional prostate cancer tests, which may include:
You should get the results of your PSA test within a week. A healthcare provider may contact you to schedule a follow-up appointment to discuss your results.
Elevated PSA levels aren’t a guarantee you have prostate cancer. There’s no specific PSA level that indicates whether you have prostate cancer or not. The only way to know for sure that you have prostate cancer is to get a prostate biopsy.
A PSA level between 4 and 10 means you have over a 25% chance of having prostate cancer. If you have a PSA level greater than 10, you have over a 50% chance of having prostate cancer. It’s very important to talk to a healthcare provider about a prostate biopsy if your PSA is in these ranges.
Advertisement
Contact a healthcare provider about a PSA test if you have:
PSA levels above 10 ng/ml typically indicate a higher risk of prostate cancer.
The early stages of prostate cancer usually don’t have warning signs.
As prostate cancer progresses, you may develop the following symptoms:
Advertisement
There’s no guaranteed way to lower your PSA levels. However, some research suggests that changes to your lifestyle and diet may help reduce your PSA levels. These tips include:
A prostate-specific antigen test provides important information about your prostate health. It’s a good idea to get regular PSA tests once you reach your 50s. However, if you have elevated risks, talk to a healthcare provider about getting a PSA test earlier. Ensure you follow the provider’s instructions before the test to get the most accurate results. If you have any questions, a provider is available to answer them.
Last reviewed on 03/21/2024.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.