The risk of infection makes fast and thorough treatment critical

The cat you’re petting purrs with delight as you gently stroke its fur. Mr. Whiskers seems so cuddly and content — right up until the moment they turn and sink their sharp fangs or claws into your skin.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
What you do next to treat your wound is very important.
That’s because cat bites and scratches bring a high risk of illness (and ickiness) from bacteria. It’s estimated that 20% to 80% of reported cat bites become infected, according to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
We asked emergency medicine physician Stephen Sayles III, MD, to explain the risks of cat bites and scratches, and what you can do to best protect yourself.
The inside of a cat’s mouth isn’t exactly the cleanest environment. It’s loaded with about 200 types of bacteria — some of which can cause a serious reaction when injected into your body via razor-sharp teeth.
Scratches come with infection risk, too, given that cat claws also carry a variety of bacteria from padding around in the world.
Bacterial infections and puncture wounds or gashes from cats can be severe, warns Dr. Sayles. The risk of complications from an infection rises if you’re immunocompromised or have diabetes.
“See a doctor within eight hours to cut your infection risk,” he advises. “You may need intravenous [through a vein] antibiotics or — in some cases — you may even need to be hospitalized.”
One study found that 30% of people who sought treatment for a cat bite on their hand ended up being hospitalized. The average stay was more than three days.
Advertisement
Bacterial infections associated with cat bites and/or scratches include:
Signs of infection from a cat bite or scratch can begin appearing within a few hours of the feline encounter. It may take as long as 10 days for symptoms of cat scratch fever to show. Rabies can take weeks or months to progress.
Given concerns about bacteria, cleaning the wound is the No. 1 priority when treating a cat bite or scratch.
Start by rinsing the wound with water to flush out as much bacteria as possible, instructs Dr. Sayles. Be gentle to avoid pushing bacteria deeper into the wound.
Next, wash the wound with soap and water. Slow the bleeding with a clean cloth and apply an over-the-counter antibiotic cream if you have it, he recommends. Then, wrap the wound in a sterile bandage.
Keep the wound bandaged until you see a healthcare provider. Again, the goal should be to get professional treatment within eight hours to help reduce the risk of infection.
A provider will likely do the following:
Plan to change your bandage several times a day as the wound heals. Watch for signs of infection — including redness, swelling, increased pain and fever — in the days that follow, says Dr. Sayles.
Even though a cat may seem sweet when it’s purring or softly meowing, the reality is that they can bite and scratch. You can reduce your risk of being wounded and infected by a cat fang or claw by:
Advertisement
In addition, always wash your hands after touching a cat and after cleaning their litter box.
Advertisement
Learn more about our editorial process.
Advertisement

This persistent myth isn’t true and can actually cause more pain than relief

Poisons are inhaled, ingested or absorbed by your skin, while venoms are delivered by bites and stings

An urgent care physician weighs in on what to do
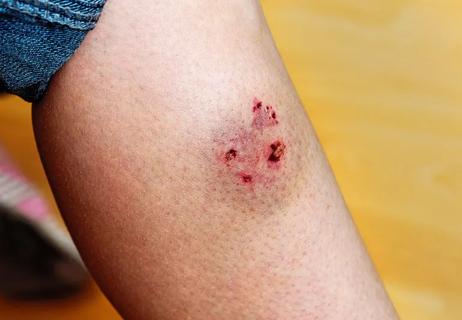
Infection is the biggest danger

They can feel similar, but the differences matter — especially if you’re at higher risk for complications

Understanding how your health information is recorded can help you take charge of your care

Yes, but symptoms can be easy to miss

Wait a few hours, then start with water or ice chips, graduating to clear liquids and then, soft, bland foods

Wearing a scarf, adjusting your outdoor activities and following your asthma treatment plan can help limit breathing problems

Your diet in the weeks, days and hours ahead of your race can power you to the finish line

When someone guilt trips you, they’re using emotionally manipulative behavior to try to get you to act a certain way