Bug bites create tiny openings in your skin that can let in dangerous bacteria
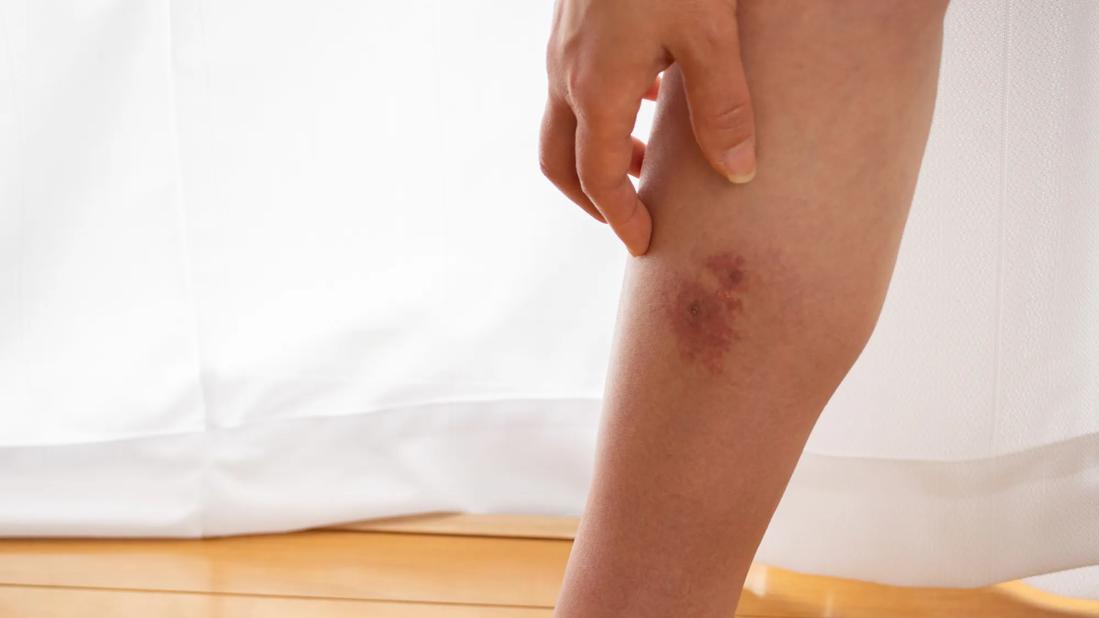
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/b172ccb8-cf97-4748-ada5-111bbc26ed5f/leg-cellulitis-1320711623)
Cellulitis on a leg from an infected bug bite
We all know that bug bites can be irritating. And you probably know that scratching at those bites isn’t a good idea.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
But do you know why? It’s because bug bites can get infected. And itching only makes infection more likely. And when you get an infection from a bug bite, it can be bad news.
Dermatologist Melissa Piliang, MD, explains how bug bites can put you at risk for cellulitis and what you can do about it.
Bug bites create teeny holes in your skin that can allow bacteria to fall in. If you scratch the bite, that opens up your skin more, creating even bigger opportunities for germs to get in and set up shop.
“If you pick at or scratch an itchy bug bite, you provide an opening for bacteria to enter the skin and tissue underneath,” Dr. Piliang explains. “The bacteria may come from under your fingernails or another source.”
Among those other sources? Prepare yourself because things are about to get a little ... gross.
Remember that kid’s book Everyone Poops? Bugs are no exception. When they land on you and go in for a bite, they can poop, too. And that tiny puncture wound is still big enough for the poo to just drop right in ... or get smeared in when you go to scratch or rub.
Bacteria like Streptococcus (strep) or Staphylococcus aureus (staph) can enter your skin after a bug bite. Once inside, they start laying the groundwork for the skin infection cellulitis, which can make you sick.
Advertisement
Symptoms of cellulitis from an infected bug bite include:
Just about any bug bite can potentially become infected, including bites from:
It’s worth noting that bug bites aren’t the only way to get cellulitis. Any open wound or scratch can allow bacteria in and lead to cellulitis. It can also happen if your skin isn’t kept clean.
Cellulitis is a bacterial infection that requires medical attention and, likely, a round of antibiotics. Left untreated, cellulitis can spread and become more severe, so it’s important not to let it fester. In rare cases, it can lead to infections in your blood (sepsis), bones (osteomyelitis) and more.
If you think you have an infected bug bite, Dr. Piliang suggests monitoring it for signs it’s spreading. “You can use a washable marker to draw a border around the bite to track its size. Contact your healthcare provider immediately if redness, swelling or blisters expand outside the border.”
Also contact a provider if you experience symptoms of cellulitis mentioned above.
What can be done for an infected bug bite?
Remember, bugs themselves don’t transmit cellulitis. So, you can take steps to reduce your risk for infection.
Advertisement
A bug bite can seem like nothing more than a minor annoyance. And often, that’s all it is.
But if you have a bite that becomes red, swollen or painful, don’t ignore it. An infected bite can lead to cellulitis, a serious condition that needs medical treatment. If you’re concerned, contact a healthcare provider — and try not to scratch.
Advertisement

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about our editorial process.
Advertisement
Keep ‘mozzies’ at bay by avoiding scented body products, beer and certain colored clothes
Vanilla extract won’t keep mosquitoes away for long, if at all — and could even attract other bugs, like wasps or flies
Alpha-gal syndrome has become more common and is a leading cause of anaphylaxis
These red, raised bites often show up in a zigzag pattern on areas of your skin that come into contact with bedding
Twice daily tick checks, the right bug sprays and long pants can help you prevent tick-borne diseases
Using insect repellent, covering up and keeping your property dry can help keep the buggers at bay
Kissing bugs are insects that can carry a dangerous parasite that causes Chagas disease
Whether you scrape or pull out the stinger, the key is to do it quickly
Although it could be used as a moisturizer, this new trend is not recommended
Communicating clear limits helps protect your time, energy and emotional well-being
High cholesterol can be genetic, but testing and treatment can lower your heart disease risk