Back injury red flags and warning signs

Whenever you step out onto the playing field or into the gym, you run the risk of suffering some sort of injury. Back injuries are among the most common, whether you’re a committed and competitive athlete or a weekend warrior.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
According to spine health expert Kush Goyal, MD, about 90% of these acute back injuries will get better on their own, typically in about three months. However, sometimes back injuries can be a bit more serious and require a doctor’s care.
Sports-related back and spine injuries vary somewhat with the sport, but a few of the most common include:
1. Cervical (neck) injuries. Some injuries occur more often in certain sports. For example, in football, we commonly see ‘stingers,’ which is a type of neck injury. These injuries manifest as transient unilateral numbness or tingling in the shoulder due to a stretching or compressing of the cervical nerve roots.
When a player suffers a “stinger” on the field, it should resolve very quickly. If not, the athlete needs immediate medical attention and further evaluation, Dr. Gladden warns.
2. Lumbar (lower back) sprains and strains. You could get one of these injuries in the gym if you try to lift too much weight or use improper technique when lifting.
Acute injuries like lower back sprains and strains typically resolve on their own. Often, you don’t need a doctor to evaluate them further.
“Treatment for minor lower back pain is generally self-directed. For these types of injuries, you can take over-the-counter anti-inflammatory medications like ibuprofen or naprosyn,” says Dr. Goyal.
Advertisement
3. Fractures and other injuries to the spine’s supporting structures. In sports that involve repetitive extension movements, such as volleyball, gymnastics, diving, cheerleading and dancing, spine stress fractures are fairly common.
“Also called pars fractures or spondylolysis, these occur when there is a crack in the bony rear portion of the spinal column,” says Dr. Goyal. “Excessive and repeated strain to the area of the spinal column known as the pars interarticularis is to blame. This type of injury causes lower back pain.”
Doctors diagnose spine stress fractures by reviewing an x-ray or CAT scan and usually treat the injuries with a back brace and rest. However, in certain instances these injuries require more aggressive treatment.
Let’s say you’ve injured yourself playing a weekend game of tackle football, or hurt your back when doing back squats at the gym. Now you’re in pain and don’t know whether you should see a doctor or just take some over-the-counter pain medication and wait it out.
If you experience any of these warning signs, you should probably get to a doctor for further evaluation:
“One of the worst things you can do if you have an acute back injury, stay in bed and remain inactive,” he says.
The muscles and supporting structures of the back weaken when you remain in bed for days on end. This can lead to a vicious cycle of continued back pain.
There are ways to reduce your risk of suffering a serious back injury. Try these suggestions:
Participating in sports is a great way to stay fit and emotionally healthy, regardless of age. Don’t let a back injury keep you out of the game.
Advertisement

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about our editorial process.
Advertisement

Hanging upside down for any length of time may decompress the tension in your spine

Drinking alcohol can cause nerve pain, dehydration and weight gain, which can all lead to back pain

Your sleep position, immobility, mattress and underlying conditions can all cause morning back pain

Rest may be all you need to get rid of running-related lower back pain
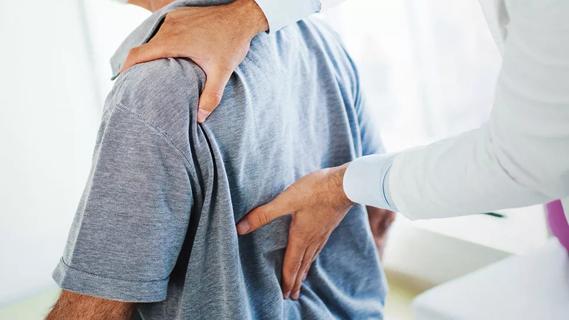
It’s always a good idea to let a healthcare provider know about any back pain you’re experiencing, especially if it results from trauma or persists longer than three months

From physical and biofeedback therapy to nerve ablations and blocks, there are many nonsurgical options for managing back pain

Rest, physical therapy, acupuncture and nerve blocks are just a few ways to find relief

Get moving, use cold packs, and try yoga and stretches to ease back pain

Even small moments of time outdoors can help reduce stress, boost mood and restore a sense of calm

A correct prescription helps your eyes see clearly — but as natural changes occur, you may need stronger or different eyeglasses

Both are medical emergencies, but they are very distinct events with different causes