Yes, it’s safe for babies starting at about 9 months old and can help clear nasal mucus
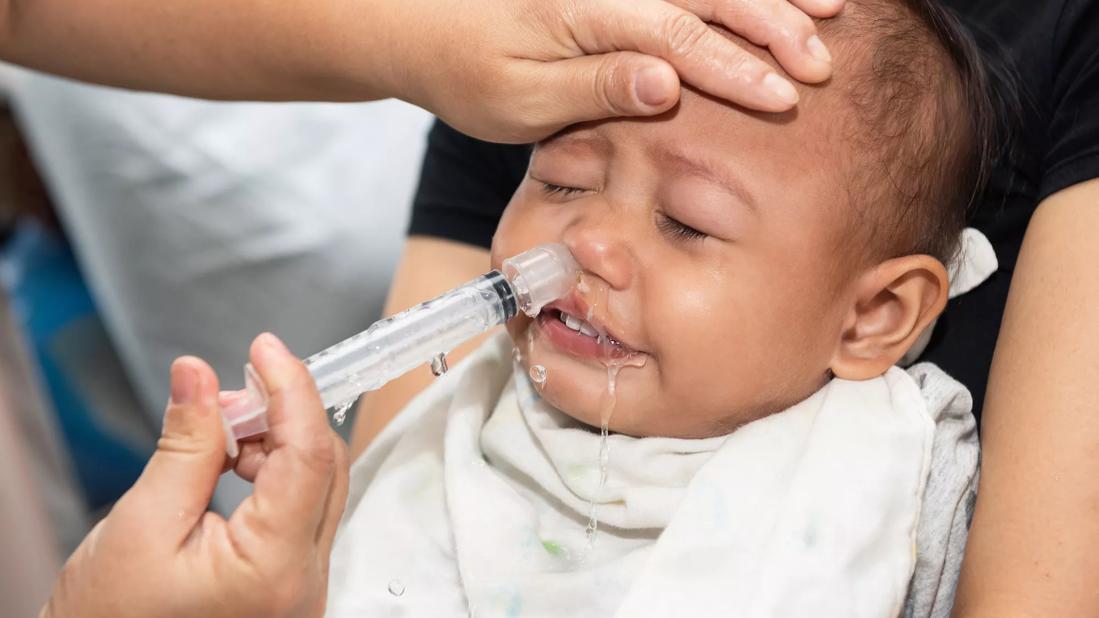
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/40606347-7df2-438a-a78d-2fe7fad00ad1/baby-nasal-irrigation-1283605631)
Baby getting nasal irrigation
When your baby’s nose is crusty and full of mucus, it can be hard for them to breathe, eat and sleep. (Which means you’re probably not too well-rested either.) Wouldn’t it be nice to flush all that snot away?
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Nasal irrigation is a centuries-old practice of using a salt (saline) solution to rinse the nasal passages. It’s an effective at-home treatment for allergies and upper respiratory infections — and it’s even safe for babies.
“Young children can’t blow their noses,” says pediatrician Lisa Diard, MD. “Nasal irrigation can reduce mucus and open their nasal passages. It’s also been shown to reduce the need for over-the-counter and prescription medications, including antibiotics.”
Dr. Diard explains how to flush your baby’s nose and at what age you can start.
It’s important to take special care when preparing for nasal irrigation. Young children’s immune systems are still developing, says Dr. Diard. To protect your baby’s health, make sure to carefully follow instructions for mixing the saline solution and flushing the nasal passages.
The saline solution in nasal irrigation matches the natural saltiness of your baby’s body.
“Salt water is soothing to sinus tissues, compared with plain water, which can cause irritation and dryness,” explains Dr. Diard.
To make the saline solution for nasal irrigation:
Advertisement
The sinuses are connected spaces. Nasal irrigation takes advantage of the link between the right and left nasal passages. You introduce fluid into one nostril and it drains out the other side — carrying mucus and debris with it.
There are many types of nasal irrigation devices. Make sure to get a device designed for babies. It’ll have an irrigation tip that fits into your baby’s nostril. The most common devices are:
To flush your baby’s nose:
Repeat up to three times per day.
Nasal flushes are best for children who can sit up and lean forward. For most babies, that’s at about 9 months, says Dr. Diard.
Nasal irrigation is safe for babies. The main risk is introducing harmful bacteria into your baby’s sinuses. Using clean equipment and sterile water reduces that risk.
Dr. Diard also recommends checking with your child’s healthcare provider before nasal irrigation if your child has:
If your child isn’t quite ready for nasal irrigation, Dr. Diard recommends other strategies, such as:
Many parents think young children won’t be able to tolerate nasal irrigation.
“Most children do very well,” reassures Dr. Diard. “Before trying nasal irrigation, I often suggest using saline nasal drops and a suction bulb. This can help a child get used to having fluid in their nose and make nasal irrigation easier.”
Advertisement

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about our editorial process.
Advertisement
Neti pots can be useful for sinus pressure relief and removing excess mucus
Most teething symptoms are mild — fevers and other major symptoms are likely something else
Most kids start losing baby teeth around age 6 — but there’s some wiggle room in the timeline
Gentle care, like moisturizing, washing and soft brushing, can help clear up cradle cap
Most babies will crawl between 7 and 10 months old, but later can be normal, too
Babies are born with very little of this vitamin, which plays a critical role in the blood clotting process
Start weaning your toddler off daytime pacifier use by 12 months old to help prevent dental issues and speech delays
Adding extra formula, cereal or medications to your baby’s bottle is a dangerous and misguided practice
Prioritize your health by managing stress, strengthening your social connections and getting quality sleep
Bolsters, blankets, pillows and blocks can offer extra support, stability and comfort
Allergies, postnasal drip, asthma or reflux could be to blame for a cough that won’t quit