Vaginal dryness, cervicitis, infections or other cervical issues could be the culprit
Seeing bright red blood after sex can be alarming. Vaginal bleeding or spotting that occurs after intercourse is known as postcoital bleeding. Bleeding after sex can happen as a result of menstruation, vaginal dryness, inflammation, infection or cervical problems.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Most of the time, it’s nothing serious. But bleeding or spotting after sex can sometimes signal larger issues, especially if it’s happening consistently.
Ob/Gyn Erin Higgins, MD, explains some of the common reasons why you may be bleeding after sex and when treatment is necessary.
If you notice bleeding after sex (or even bleeding during sex), you may ask yourself: Why am I bleeding after sex?
Vaginal bleeding is different from postcoital bleeding. Postcoital bleeding is related to a number of conditions that can be infectious or noninfectious.
“With infectious causes, we’re always concerned about genital tract infections,” says Dr. Higgins. “For noninfectious causes, doctors are concerned about vaginal atrophy, cervicitis and other cervical conditions.”
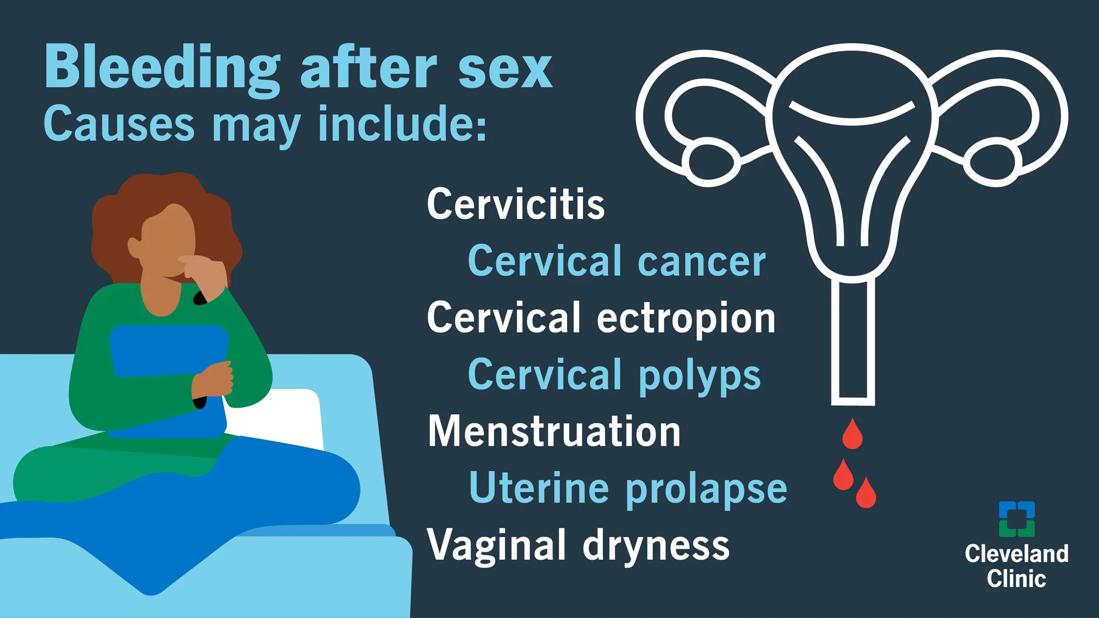
Here are seven common causes of postcoital bleeding.
This may seem obvious, but before you call a doctor, consider whether it’s around that time of the month.
“If you have sex right before or after your period, that may explain your bleeding,” notes Dr. Higgins.
Keeping track of your cycles with a menstrual calendar is helpful for resolving such questions and understanding more about what’s happening during your menstrual cycle.
Also commonly referred to as vaginal dryness, vaginal atrophy is a condition where the skin of your vagina gets drier and thinner, typically because of a lack of estrogen. Women of all ages can experience vaginal atrophy, though it most often shows up after menopause. This dryness can also affect the vulva.
Advertisement
“If dryness is severe, the friction may cause bleeding after intercourse,” explains Dr. Higgins. “Using lubrication before or during sex may help, but your doctor may recommend hormone replacement therapy if lubricants aren’t sufficient.”
Cervicitis is inflammation of the cervix, often as a result of infections or irritation. This condition may cause bleeding or a change in vaginal discharge. Possible causes include:
Although the bacterial and viral infections that cause cervicitis are contagious, this condition can be treated with antibiotics or antifungals.
With cervical ectropion, the soft, glandular cells that line the inside of your cervical canal expand into the outer part of your cervix (where the cells are typically hardier), almost as if it’s turning itself inside out. This is a normal condition for many and usually doesn’t require treatment.
But if there are symptoms, such as excessive discharge or bleeding, it could require outpatient heat or cold therapy to treat the area and stop the bleeding.
“If you have bleeding or pain from cervical ectropion that interferes with your sex life, your doctor may recommend treatment,” shares Dr. Higgins.
These are growths on the opening of your cervix that sometimes result from chronic inflammation or hormonal changes. Almost all cervical polyps are benign. If your symptoms are minor, you may not need treatment.
Sometimes, with irregular bleeding, there’s a small chance of abnormal cells developing. In these cases, your polyps are removed and sent for evaluation to make sure those cells are benign. You may also need to have any polyps removed if you experience frequent spotting or cramping.
While rare in younger women, uterine prolapse (when your uterus comes out of its normal position) occurs more often after a hysterectomy, and tends to develop slowly over time.
For a minor prolapse, your doctor may recommend weight loss or Kegel exercises to strengthen muscles in the area. If your uterine prolapse is severe enough, it may cause bleeding. Your doctor can insert a ring to support the tissue or perform surgery to repair it.
Advertisement
About 11% of women who have cervical cancer have postcoital bleeding, according to Dr. Higgins. In fact, it’s often the first symptom of cervical cancer and may be one of the things you’re most worried about.
“Cervical cancers are preventable in most cases as long as you follow up with your gynecologist and have routine Pap and HPV screenings done. Cervical cancer tends to be very slow growing over many years,” clarifies Dr. Higgins. “Most people with postcoital bleeding don’t have cervical cancer.”
If you’re diagnosed with cervical cancer, your doctor will refer you to a gynecologic oncologist for further management. A simple outpatient treatment can remove abnormal precancerous cells. If the cells are cancerous, your gynecologic oncologist will likely recommend chemotherapy, radiation, surgery or a combination of treatments depending on your condition.
A good rule of thumb is that any abnormal bleeding, whether it’s just a few drops or a large amount, needs to be evaluated, Dr. Higgins states.
Very light bleeding or spotting can also happen if a fertilized egg implants itself along the lining of your uterus. Known as implantation bleeding, this is one of the first signs that you may be pregnant. If you notice bleeding after sex and your period is late, it’s important to take a pregnancy test.
Advertisement
Are you experiencing pain and bleeding or heavy bleeding? If so, it’s time to get it checked out.
“If you’re experiencing something that isn’t normal, it’s not necessarily bad, but if it’s consistently happening or you’re just concerned, get it checked out,” advises Dr. Higgins.
A visit to a healthcare provider can answer many of the questions you may have, like: Why do I bleed after sex? Is spotting after sex normal? If I notice light spotting after sex, could I be pregnant?
During your visit, your doctor will go over your medical history and ask about:
A physical exam will check for signs of infection. If your Pap test isn’t current, your doctor can perform one for you while you’re in their office. A Pap screening can help determine the need for any further tests or procedures.
If your testing shows no problems, but your bleeding continues — and it only occurs after sex — they may suggest other tests. This may show any underlying condition that a physical exam and Pap smear didn’t find.
“Your doctor will outline any necessary testing you may need,” says Dr. Higgins. “The important thing to remember is that most of the time, it’s nothing serious.”
Advertisement

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about our editorial process.
Advertisement

Watery discharge is usually normal and may happen more when you’re ovulating

Decode your discharge and what it means for your health

It’s not always a cause for alarm, but it could be a yeast infection

It usually happens when blood mixes with vaginal fluid, but not always

Most oropharyngeal cancers can be traced to a virus that can be shared during oral sex

It’s important to angle it toward your rectum or back, along the natural curve of your vaginal canal

To help manage symptoms, switch to more absorbent period products, make healthy lifestyle changes and explore treatment options

Yes, you can pee with a tampon in; no, they won’t stretch out your vagina or make cramps worse!

Even small moments of time outdoors can help reduce stress, boost mood and restore a sense of calm

A correct prescription helps your eyes see clearly — but as natural changes occur, you may need stronger or different eyeglasses

Both are medical emergencies, but they are very distinct events with different causes