Postherpetic neuralgia is challenging, but help is available
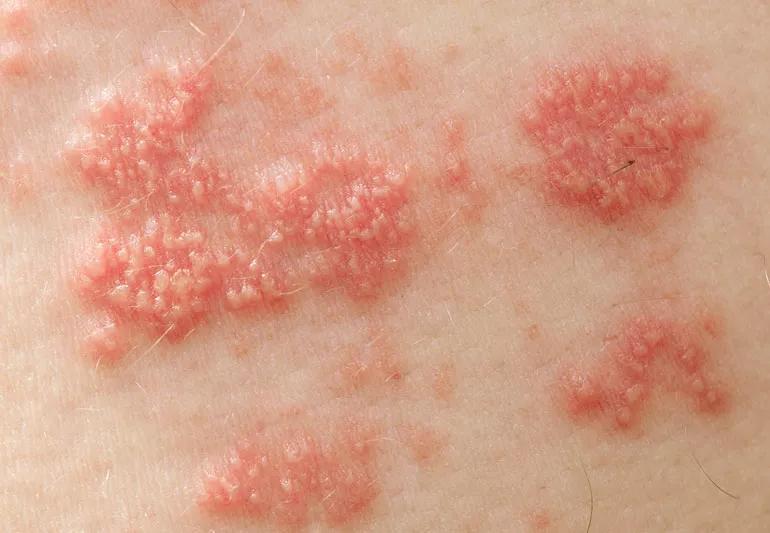
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/cd15ebb7-6f6e-4a8a-ad44-e4ecce052f23/shinglesVirus-177384156-770x533-1_jpg)
shingles virus on skin
Dealing with a case of shingles is painful enough. But once the skin rash resolves, a chronic pain syndrome called postherpetic neuralgia (PHN) can sometimes develop.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Studies suggest that roughly 30% to 60% of people over age 60 who get shingles — caused by the chickenpox virus, herpes zoster — go on to develop PHN.
Many things remain a mystery about this chronic condition, in which the herpes zoster virus affects the nerves and causes pain, usually involving the chest wall. It causes a burning or stabbing sensation in the area where the shingles outbreak first occurred.
“We don’t know why some people get post-herpetic neuralgia and some don’t,” says pain management specialist Ellen Rosenquist, MD. “There’s plenty of speculation. The nerves may become more sensitive, or the virus may be reaching and damaging the central nervous system.”
Fortunately, early treatment for shingles can lower your chances of getting PHN.
“For some people, the pain becomes refractory, or resistant to treatment,” explains Dr. Rosenquist. “So we want to treat shingles as fast as we can — ideally as soon as somebody feels a tingling or burning sensation, even before a rash develops.”
She adds that whenever nerve pain is involved, some people respond to treatment and some don’t. (The virus cannot be removed from the nerves.)
However, medications taken orally or injected that can target the affected nerves may be able to “stun” the nervous system into behaving properly. That means transmitting the appropriate signal to the brain.
“It’s like restarting a computer,” Dr. Rosenquist says. “When it’s running slowly or acting weird, you restart it. We are trying to turn that nerve off. When it comes back on, hopefully, it will send an appropriate transmission as opposed to a pain transmission.”
Advertisement
Treatment options for PHN patients include:
Patients with refractory PHN rarely need opioid (narcotic) pain medication. “However, you should be evaluated by a physician. We can’t make a blanket statement about treatment. It is individualized,” she says.
If you are age 60 or over and have not had shingles, talk to your doctor about getting the shingles vaccine. Not only will it reduce your risk of developing shingles, but if you do develop shingles, you’ll be more likely to have a mild case. And, just as important, you’ll be much less likely to develop PHN if you’ve had the vaccine.
Advertisement

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about our editorial process.
Advertisement
If you have a weakened immune system, your risk for getting shingles a second or third time increases
It’s 97% effective in preventing shingles in people between the ages of 50 and 69
But if you haven’t been vaccinated, you could get chickenpox from somebody with shingles
You may be surprised to learn that acupuncture usually doesn’t feel like anything — and any discomfort is typically brief
Gallstones can block bile in your biliary system and lead to pain and discomfort
This chronic condition most commonly causes pelvic pain and severe cramping during periods, but it can bring other types of pain symptoms, too
Your knees could be hurting at bedtime because of inflammation, injury or some other condition that gets worse with pressure and positioning
Spinal blocks provide complete numbing for shorter periods, while epidurals can allow for some feeling
Getting back to normal after a head injury takes time — and patience
Dressing in multiple layers, drinking warm liquids and taking breaks indoors can help prevent these cold-weather injuries
Pick bell peppers to help fight cancer, memory decline and joint pain