Several options to help get you moving
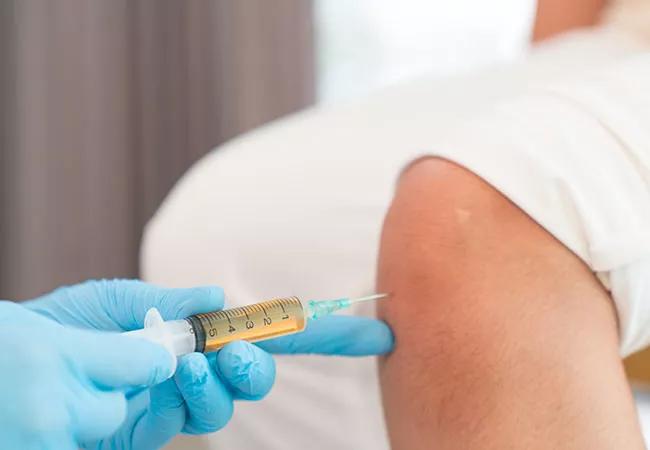
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/fb6f569d-6a23-4e12-9c4a-baabcee9386d/Joint-Pain-Knee-Injection-650x450_jpg)
Joint Pain Knee Injection
If you’re one of the 30 million adults in the United States who live with joint pain, you know it’s often debilitating. It can keep you from staying active and even make daily chores seem impossible. What you might not know is that your doctor can treat you with more than pills or surgery.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Depending on the severity of your pain, injections can be another option for easing your joint pain and get you moving again, says sports and medical orthopaedist Jason Genin, DO.
“In many cases, we use these injections to try to reduce inflammation and pain in your joints,” Dr. Genin says. “With some treatments, you often can experience fewer symptoms for several months.”
There are several injectable options to help treat knee pain. “The injections range from corticosteroids, which have been around for decades, to newer cellular therapies like platelet-rich plasma (PRP),” he says.
Your physician will decide which one is best based on your individual needs, says sports and medical orthopaedist Dominic King, DO.
“Not every injection is right for every patient,” Dr. King explains. “We take a lot of time to understand your specific issues and create an injectable plan that works with your entire knee care path.” This can include weight loss, exercise, stretching, activity modification, anti-inflammatory medications, as well as injection therapy.
Traditional injections, such as corticosteroids (“cortisone”), can be effective — particularly in the late stages of arthritis, as a way to get past a sudden increase in pain and delay the need for surgery.
Advertisement
Hyaluronic acid (HA) injections often are used when corticosteroid injections don’t work. But they usually are approved only for use in the knee.
In some instances, doctors consider HA injections first if you don’t have obvious signs of inflammation. HA also is a better option if you have diabetes, as corticosteroids can raise blood sugar levels.
Also known as gel injections, HA injections are chemically similar to your natural joint fluid.
When you have osteoarthritis, joint fluid becomes watery. So, this injection helps to restore the fluid’s natural properties and works as a lubricant and a shock absorber.
“HA is a cushion or a buffer against inflammatory cells in the joint,” Dr. Genin says. “In some cases, it can stimulate the knee to start producing more natural HA.” Some physicians also believe that HA helps reduce pain by coating nerve endings within the joint.
One treatment, which may consist of between one and three injections, usually offers symptom relief for four to five months, but sometimes up to one year. However, pain and stiffness will return. Most insurance companies only approve one HA injection every six months.
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injections are a newer alternative to treat osteoarthritis joint pain. Cells from the patient’s own blood are processed in a centrifuge to remove red blood cells and most white blood cells, concentrating the platelets. “A growing body of evidence has shown that PRP can be as effective or more effective than anti-inflammatory medications or cortisone, particularly in the early stages of arthritis,” Dr. Genin adds.
Side effects include a very low risk of infection and pain at the injection site. You also must stop taking oral anti-inflammatory medications for a short amount of time if you get a PRP injection, Dr. Genin says.
“Often, many of these injections are effective in reducing or stopping your joint pain, but it’s important to remember that they may not keep the pain from returning, Dr. King notes. In fact, they’re most effective when used with other therapies. And we consider surgical options only if other treatment options have failed.”
Advertisement

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about our editorial process.
Advertisement
Some creakiness is typical after rest, but longer-lasting stiffness may be other issues
Barometric pressure can play a role in joint pain, but that doesn’t mean you have to live with it
What you need to know about prosthetic joint infection after surgery
Even one less pound helps preserve hips and knees
Getting the facts straight about osteoarthritis
Spinal blocks provide complete numbing for shorter periods, while epidurals can allow for some feeling
Try seated and standing exercises to help lengthen and strengthen the muscles that support your plantar fascia
This medication is best used on a limited basis
Prioritize your health by managing stress, strengthening your social connections and getting quality sleep
Bolsters, blankets, pillows and blocks can offer extra support, stability and comfort
Allergies, postnasal drip, asthma or reflux could be to blame for a cough that won’t quit