Letting your baby feed themself foods the whole family enjoys has its benefits — but stick to softer foods and follow safe-eating guidelines
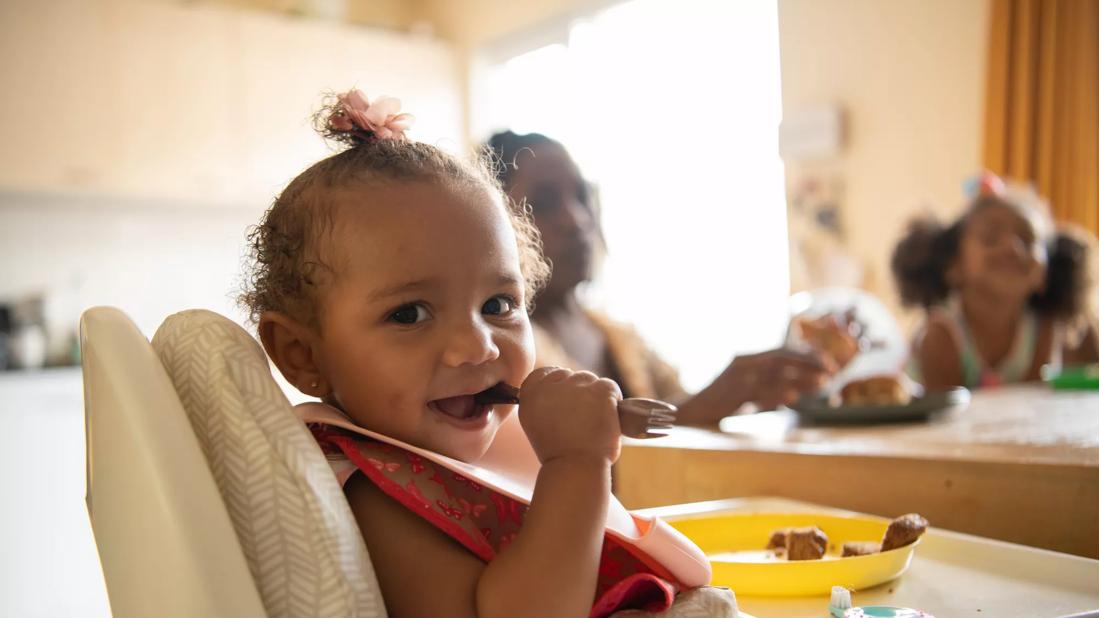

During their first few months of life, your baby has already had so many exciting firsts: First smiles, first laughs, first time sleeping through the night (hallelujah!).
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
And as they grow, they start to develop some important life skills. Among them: How to feed themselves.
Getting your baby started with solid foods is exciting. But it can also bring on a lot of questions.
When should I transition my baby to solid food? What foods should my baby be eating? What to do about potential allergens?
There’s no one “right way” to transition from a diet of only breast milk and/or formula to one with new foods, textures and flavors. But there are some best practices for how and what to feed your little one.
One option is baby-led weaning, or BLW for short, and it has its advantages. We talked with pediatrician Kimberly Churbock, MD, about what baby-led weaning is and how to safely introduce your baby to foods.
Baby-led weaning puts babies in charge of mealtime. That can mean skipping spoon-feeding pureed foods and jumping right into enjoying solids with the rest of the family.
“With baby-led weaning, instead of buying or making specific foods to feed your baby, you’re preparing the same meal for the whole family, with modifications as needed for your newest eater,” Dr. Churbock explains.
Baby-led weaning is about providing foods that are nutritious for babies in a way that they can handle them.
Advertisement
Sure, your 6-month-old might not be picking up a turkey burger on a bun, loaded with fresh toppings. But cutting up a patty and letting them chow down? Yep!
“With baby-led weaning, you’re incorporating baby into family mealtime from the get-go, allowing them to eat some of the same foods that the rest of the family is eating,” Dr. Churbock clarifies. “But being mindful of portions for your littlest eater, and what’s going to be safe and appropriate for them.”
Dr. Churbock shares a few ways that baby-led weaning can be a big win for families and babies alike.
When everyone in the house is eating the same (or similar things), you cut down on meal prep time and are likely saving some money.
Because having separate meals for babies can be a real drag. After all, other people in your family need to eat, too. And they’re probably not looking forward to a jar of pureed string beans.
“Prepared baby food can be expensive. And making your own can be a time commitment” Dr. Churbock acknowledges. “If you’re preparing the same food for the whole family, you’re not necessarily having to buy something separate and special.”
Baby-led weaning brings baby to the table. Literally.
When baby can sit and eat with others, it’s a chance to start off normalizing the experience of family mealtimes.
“Whenever possible, it’s wonderful for families to eat together,” Dr. Churbock advocates. “By being part of the mealtime, babies can see role models for how to chew and how to swallow. They learn a lot by watching us eat.”
Whether you’re making your own purees or buying packaged baby food, your baby is only trying one texture of food. Something akin to pudding.
Sure, the flavors may change. But the mouthfeel? All the same.
But purees aren’t the only style of food that babies can have. And with baby-led weaning, you expose your little tot to a broader array of tastes and textures. Foods more like those they’ll be eating for the rest of their lives.
Allowing baby to feed themselves similar foods to those on your own plate can help them develop some age-appropriate (and highly useful) skills.
For starters, baby-led weaning can let babies gauge their own appetites.
“Over time, they can learn to self-regulate,” Dr. Churbock says. “They’re not going to overeat because they’re in control of what’s going in their mouth and what they’re swallowing.”
What’s more, it gives baby a chance to flex their fine motor skills. (The same skills they’ll need to do things like use scissors, brush their teeth and tie their shoes when they’re bigger.)
Advertisement
“They’ll practice picking up a piece of food, bringing it to their mouth, manipulating it to get it into the mouth, chewing and swallowing,” she continues. “All of those actions require fine motor skills and oral motor skills.”
Most babies will be ready to try baby-led weaning as soon as they’re able to start solid foods. For most babies, that’s around 6 months old or older. (Not earlier. The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends only breast milk and/or formula until the 6-month mark.)
Some babies may need more time, though.
“Every baby is different,” Dr. Churbock points out. “If your baby was born prematurely, you may see signs of readiness closer to their corrected age of 6 months, rather than their chronological age of 6 months.”
If you’re concerned about your baby’s readiness for foods at the 6-month mark, talk with your child’s healthcare provider, like their pediatrician or a speech pathologist. That can be especially important if your baby has health conditions that could impact their ability to eat or to feed themselves.
Watch for these signs that it could be time to let your baby take control of feedings:
Advertisement
And even if you want to try baby-led weaning, that doesn’t mean you have to ditch the purees altogether.
Try small steps. For example, you might help a baby hold a spoonful of puree, but then hand it over and let them work on moving it to their mouth on their own.
“It’s about following the baby’s lead,” Dr. Churbock notes. “That means watching for signs of developmental readiness and, when a baby is ready, allowing them to self-feed.”
Remember, too, that breast milk or formula (or some combination of them) should still be your baby’s primary source of nutrition until their first birthday.
So, no need to fret if baby doesn’t actually consume much food when first starting solids.
“It can take some time for babies to figure out complementary food feeding, and that’s OK,” Dr. Churbock says. “Breast milk and formula remain the most important source of nutrition through the first year of life.”
The best baby-led weaning foods have a few things in common. Look for foods that are:
Here are some ideas of some foods to try and avoid when you’re first practicing baby-led weaning:
Advertisement
| Category | Foods to try | Foods to avoid |
|---|---|---|
| Fruits | Bananas, pears, avocados, kiwi, mango, applesauce and strawberries. Cut round fruits into small bites, like grapes and berries. | Round fruits that aren’t cut, like grapes or berries. |
| Vegetables | Most peeled and cooked vegetables, like cooked sweet potatoes, carrots and squash. Tomatoes cut into small bites. | Hard or textured raw vegetables, like raw carrots or celery. |
| Proteins | Ground, soft and shredded meats and fish, tofu, yogurt, well-cooked or scrambled eggs, and cheese. | Tough or chewy proteins, like steak and fish known to be high in mercury. |
| Drinks | Breast milk, formula and water. | Other milks and juice. |
| Category | ||
| Fruits | ||
| Foods to try | ||
| Bananas, pears, avocados, kiwi, mango, applesauce and strawberries. Cut round fruits into small bites, like grapes and berries. | ||
| Foods to avoid | ||
| Round fruits that aren’t cut, like grapes or berries. | ||
| Vegetables | ||
| Foods to try | ||
| Most peeled and cooked vegetables, like cooked sweet potatoes, carrots and squash. Tomatoes cut into small bites. | ||
| Foods to avoid | ||
| Hard or textured raw vegetables, like raw carrots or celery. | ||
| Proteins | ||
| Foods to try | ||
| Ground, soft and shredded meats and fish, tofu, yogurt, well-cooked or scrambled eggs, and cheese. | ||
| Foods to avoid | ||
| Tough or chewy proteins, like steak and fish known to be high in mercury. | ||
| Drinks | ||
| Foods to try | ||
| Breast milk, formula and water. | ||
| Foods to avoid | ||
| Other milks and juice. |
Dr. Churbock reminds us, too, that you don’t have to avoid pureed textures completely to do baby-led feeding. “As adults, we eat soft-textured foods, too. Soft foods like oatmeal, unsweetened applesauce, and plain whole-fat yogurt and Greek yogurt are great early foods for babies.”
As you start foods, remember that babies under the age of 1 shouldn’t be given honey, as it can carry a risk of infant botulism.
And if it’s all sounding a little ... messy. You’re right. And that’s OK.
“Expect and embrace some mess,” Dr. Churbock encourages. “Self-feeding is a great sensory experience for babies, but it’s not without some trial and error.”
Most pediatricians recommend exposing babies to potential allergens early and often. That includes things like dairy products, eggs and nut butters.
That’s because eating those foods early has been associated with preventing food allergies in some kids.
“Some allergens are also great textures for early eaters, like soft strips of egg omelet, or pieces of moist flaky fish, like salmon,” Dr. Churbock notes.
Avoid giving whole peanuts or tree nuts to your infant due to the risk of choking. Instead, these foods can be safely introduced by mixing creamy nut butter into another food that your baby has previously tried and tolerated, like oatmeal or applesauce. This helps make the nut butter less sticky and tacky. Powdered versions of peanuts and other tree nuts can be used in the same way.
If you’re concerned about the risk of food allergies, talk to your child’s healthcare provider for their recommendations.
Properly supervised baby-led feeding is safe for most babies who are developmentally ready for it. But there are some safety considerations to be aware of.
Consider these tips:
Baby-led weaning can be a big benefit for baby and the whole family. But if it’s slow-going or even isn’t working out, that’s perfectly OK.
“There are multiple healthy ways to feed your baby,” Dr. Churbock says. “Feeding methods aren’t always one-size-fits-all, and as long as you’re being safe, you don’t have to do things in a certain way.”
Learn more about our editorial process.
Advertisement

In babies under 12 months old, cow’s milk has been associated with gastrointestinal bleeding

No juice until your child is 1 year old — and even then, they shouldn’t have much, if any

Ultimately, the choice depends on what works best for you and your baby, but it’s also important to be aware of the pros and cons of both

Ideally, you want your toddler to be drinking from a ‘big kid cup’ by age 2

Levels are generally low, but there are ways to minimize potential health risks

Slowly introducing cow’s milk (or soy milk) can help your child make the change

In babies under 12 months, honey may cause a serious illness called infant botulism
A daily dose of vitamin D can help babies build strong bones, as well as boost their brain development

Wearing a scarf, adjusting your outdoor activities and following your asthma treatment plan can help limit breathing problems

Your diet in the weeks, days and hours ahead of your race can power you to the finish line

When someone guilt trips you, they’re using emotionally manipulative behavior to try to get you to act a certain way