They could help with digestion … or make existing symptoms worse
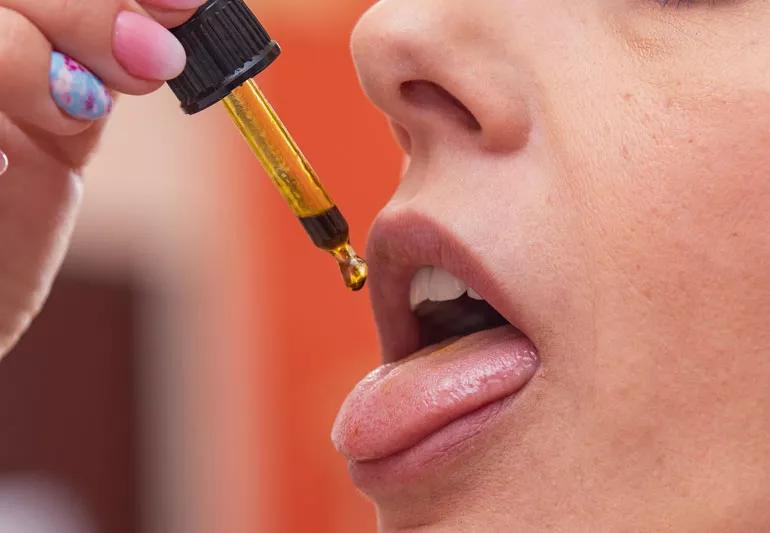
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/71121b48-a6a4-44db-88d9-a6f61954fb4b/digestiveBitters-1212980450-770x533-1_jpg)
using digestive bitters
“Bitter” isn’t typically a glowing descriptor, but the benefits of digestive bitters might make you reconsider the word. Long used in traditional Chinese medicine, it’s pretty much exactly what it sounds like: tinctures (a medical substance in an alcohol carrier) of bitter herbs said to aid and improve your digestion.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
You may already be familiar with bitters (liquor flavored with pungent-tasting plant extracts) added to fancy cocktails, and digestive bitters are actually pretty similar. Registered dietitian Beth Czerwony, RD, LD, explains what these herbal elixirs can (and can’t) do for your digestive health.
The basic idea behind bitters is that they stimulate your taste buds to create more saliva (spit), which in turn jumpstarts your digestive system. You might not realize it, but saliva is one of the keys to digestion, contributing to the breakdown of starches and fats.
Herbs commonly used in digestive bitters include:
Think about it: Cocktails that contain bitters (like negronis, Aperol spritzes and Sazeracs) are known as apéritifs, beverages you drink before a meal to rev up your digestive system.
Digestive bitters do the same thing — you just don’t need an entire glass of them. And you wouldn’t want one, either, because in their pure form, they’re much more bitter than the cocktails that sometimes contain them.
There aren’t yet enough conclusive studies that delve deep into the benefits of bitters. But the biggest reason to try them is that they may give your digestive system a boost.
Advertisement
“Some people have gastrointestinal issues due to the fact that they don’t have enough stomach acid. In these cases, bitters can help create some of that extra juice to help break down food,” Czerwony says. “They increase the amount of gastric juices in your stomach, which ultimately helps with digestion.”
Though some people believe bitters can help with weight loss, the evidence itself is slim. “Some bitters do stimulate the production of hormones in our stomach that suppress the appetite,” Czerwony says. “For the most part, though, the level of acid in bitters just kills your appetite because they don’t taste great.”
Amounts vary by product, so follow dosage instructions on the packaging. Typically, though, you’ll place a few drops (or sprays, depending on the format) onto your tongue about 15 minutes before a meal. This gives them time to kick in before you eat.
Unfortunately, there’s no way to avoid the taste of bitters, as the impact of bitterness is the whole point. “If it doesn’t taste bitter, you’re not going to get the results that you’re looking for,” Czerwony notes.
Bitters aren’t for everyone. Czerwony weighs in on who should avoid them — but first, she offers a bit of blanket advice for anyone who’s considering them.
“Like supplements and vitamins, bitters aren’t regulated by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, so you can’t know for sure what the concentrations are,” she says. “You should always check with your doctor before adding something like this into your repertoire.”
Here’s what to know about the possible risks of taking digestive bitters:
If your gastrointestinal tract is working well on its own — or if it’s already working overtime — consuming bitters may actually backfire. Bitters create more gastric acid in your stomach, which can actually contribute to digestive issues in people who are predisposed to them:
“If you’re already prone to these things, bitters aggravate them by making your digestive tract a little bit more reactive,” Czerwony cautions.
Think about bitters like you would any other supplement or vitamin — that is to say, they can interact negatively with medications you’re already taking. And again, you should always check with your doctor before giving them a try.
“Bitters can react with blood pressure medications, insulin, hypoglycemics and other medications, so it’s really important that you be cautious and talk to your doctor before taking anything them,” Czerwony advises.
Advertisement
Skip the bitters if you have any of the following conditions:
It’s also important to remember that bitters are made with alcohol, so you shouldn’t take them if you’re pregnant or nursing, or if you’re in recovery.
It should be no surprise that bitters taste, well, particularly bitter — after all, that’s the whole point. If you find that the taste just isn’t worth the potential payoff, there are still other ways to lend your digestive system a hand.
“Bitters definitely aren’t the only option,” Czerwony says. “These ingredients are found in nature, and you can work some of them into your diet pretty easily.” Foods that can aid in digestion include:
“Instead of turning to bitters for digestive benefits, you can just work them into your diet in the everyday normal route,” Czerwony advises. The bonus there? For the most part, there’s no need to check with your doctor before digging into a leafy green salad.
Advertisement

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about our editorial process.
Advertisement
Pick bell peppers to help fight cancer, memory decline and joint pain
The tropical fruit is a good source of antioxidants and vitamin C
High amounts of cholesterol and saturated fat in red meat may be linked to heart disease
The leaves and pods from this tree are rich in essential nutrients
This starchy root vegetable is a staple in many global cuisines — but it has to be prepared correctly, or it can cause serious concerns
These delicate green sprouts can give you an extra dose of vitamin K and other nutrients — but they’re not safe for everyone
Edamame, lentils and chicken breast are good sources of protein
Eating this root vegetable can help support your eye, heart and brain health
Prioritize your health by managing stress, strengthening your social connections and getting quality sleep
Bolsters, blankets, pillows and blocks can offer extra support, stability and comfort
Allergies, postnasal drip, asthma or reflux could be to blame for a cough that won’t quit