Our expert explains why swollen lymph nodes happen
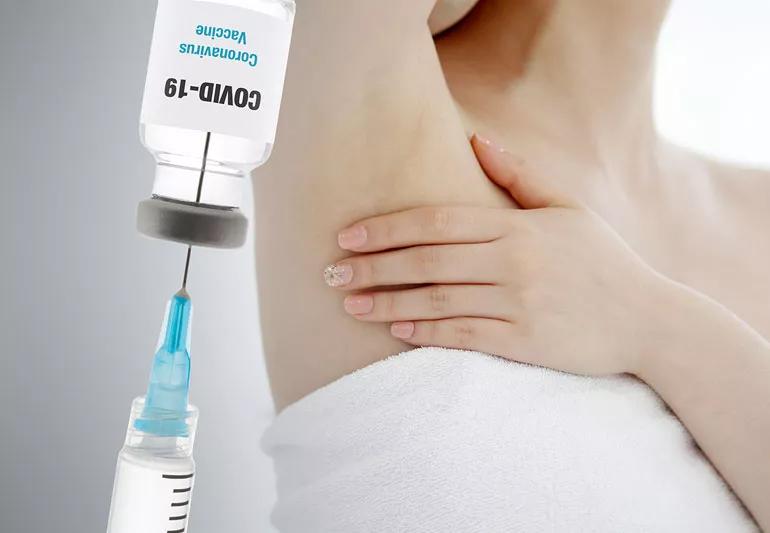
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/2b886921-f8b0-4ebd-b7f1-55e743c1b29a/covidVacLymphNodesWmn-1041403724-770x533-1_jpg)
covid vaccine swollen lymph nodes
As more people across the globe continue to receive the COVID-19 vaccine, we’ve learned quite a bit about the side effects that the vaccine can cause.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
But one side effect — swollen lymph nodes under your arms — has been getting more notice because it’s an overlapping symptom for other issues. It’s important to know what’s a side effect of the vaccine and what’s a sign of something that needs further attention.
To better understand what’s causing this symptom and what you should know before getting your COVID-19 vaccine, we talked to diagnostic radiologist Laura Dean, MD.
The most common side effects of the COVID-19 vaccine include:
The side effects are typically mild, last between 24-48 hours and are most commonly felt after the second COVID vaccine dose.
Lymph nodes are part of the body’s immune system so, according to Dr. Dean, swollen lymph nodes are a potential side effect of any vaccine. “The whole point of the vaccine is to get your immune system to mount a response to whatever the vaccine agent is,” she says.
But it seems that the COVID-19 vaccines can cause a more robust swelling in lymph nodes. And those swollen lymph nodes, like other side effects, vary from person to person. “We’re still learning about these vaccines and the side effects as more and more people receive them,” Dr. Dean says.
Advertisement
The swollen lymph nodes generally appear a few days after someone receives the vaccine, on the same side of the body as they got the shot. “We’re still watching these examples, but right now we think that symptom subsides with a few days to a few weeks,” she adds.
Swollen lymph nodes can sometimes be a symptom of cancer. But it’s important to remember that they can have a number of other causes. And while the COVID-19 vaccine appears to only cause swelling on one side, swelling in lymph nodes on both sides of the body is also not necessarily a sign of cancer.
“You see general lymph node enlargement — under the arms, in the chest or groin — with something like lymphoma,” says Dr. Dean. “But there are other reasons you’d see that, too, which are far less serious than cancer.”
Other causes of swollen lymph nodes include:
There are additional conditions, too, that Dr. Dean says healthcare providers may look into. “We address the issue by taking a very detailed patient history and looking for other conditions that may cause the swelling, like rheumatoid arthritis, lupus or autoimmune diseases.”
And, yes, this includes swelling on just one side. “We don’t want to miss something because a lymph node on just one side is swollen,” she adds. “But we’ve also added questions about recent COVID-19 vaccines to our screening questions to make sure we’re getting a full view of what might be affecting the patient.”
Still, if you’re concerned by the appearance of swollen lymph nodes within a day or two after receiving your COVID-19 vaccine, it’s worth contacting your healthcare provider. With their knowledge of your medical history, they have the necessary context to make a full evaluation.
It’s the location of the lymph nodes involved with this particular side effect that’s causing concern. Many times (but not always) the location of a person’s lymph node swelling corresponds to the site of infection. For many who have breast cancer, that includes the lymph nodes in the armpits.
“If breast cancer moves outside of the breasts, it tends to go to those patterns of the lymph fluid inside the breast tissue,” Dr. Dean explains. “It’s a very integrated system, so it’s one of the areas we closely scrutinize.”
Because early detection is so key to treating breast cancer, it’s understandable that this overlapping symptom is causing a little bit of confusion and even alarm in many patients.
The most important thing, Dr. Dean says, is that patients maintain their preventive care plan for breast cancer, especially mammogram screenings.
The Society of Breast Imaging recommends scheduling your mammogram either before your first dose of the COVID-19 vaccine or about four to six weeks following your second dose, if possible. If that’s not possible, though, it’s important to keep both your scheduled screening and your vaccine appointment.
Advertisement
“We’ll work with you to explain what’s going on, what we see and what might be a side effect,” Dr. Dean adds. “And if there’s potential overlap, you can schedule a short-term follow-up screening for a few weeks later just to be safe.”
Again, Dr. Dean stresses that there’s no reason to be alarmed about getting swollen lymph nodes from the COVID-19 vaccine. “Swollen lymph nodes after vaccination are usually a sign that your immune system is responding to the shot," she says. "While this can feel concerning, it typically resolves on its own."
Finally, she reiterates how important it is to maintain your preventative care appointments despite these side effects. “Doctors emphasize that swollen lymph nodes after vaccination aren’t usually a cause for alarm. If you’re considering a COVID-19 vaccine, it may help to talk with your provider about possible side effects and how to manage them."
Advertisement

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about our editorial process.
Advertisement
Updated vaccinations are recommended to better protect against the evolving virus
Redness, swelling, itching and rash can happen when your body’s immune system reacts to the vaccine injection
Irregularities in cycle length and flow aren’t a cause for concern
Before you panic, here are the options to consider
Just one more myth to add to the misinformation pile
Infants are at high risk of severe RSV, but getting the vaccine during pregnancy helps protect them from it
Chilblain-like skin lesions and rashes are mild (and rare) complications of many viral infections, not just COVID-19
Yes, but symptoms can be easy to miss
Getting back to normal after a head injury takes time — and patience
Dressing in multiple layers, drinking warm liquids and taking breaks indoors can help prevent these cold-weather injuries
Pick bell peppers to help fight cancer, memory decline and joint pain