Advertisement
It’s commonly mistaken for obesity

Lipedema: No, it’s not a typo. It’s a real condition that’s often overlooked or confused with lymphedema. And its hallmark is the development of too much fat below the waist.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
“Because women with lipedema are often overweight, doctors are often dismissive,” says vascular medicine specialist John R. Bartholomew, MD. But lipedema is not obesity, and it’s not always a woman’s fault that she has it.
“Doctors often don’t understand that exercising and dieting won’t get rid of this lipedema fat,” he says.
Lipedema means “fluid in the fat” and is sometimes known as the painful fat disorder. It causes excessive fat deposits on the legs, thighs and buttocks and upper arms.
“Women with lipedema frequently feel like they have two bodies,” Dr. Bartholomew explains. “They may have a typical upper body, chest and abdomen. But at their waist and below, their lower half is out of proportion to their upper half. They often have difficulty finding clothes that fit because it’s like they are two different people.”
It occurs almost exclusively in women and begins:
While doctors first recognized lipedema in the 1940s, experts still don’t know what causes it. “We think there may be a gene because it does seem to run in families,” Dr. Bartholomew says. “Often, I’ll ask a woman if her mother or other females in her family had a similar body shape.”
Lipedema isn’t rare, but it’s rarely diagnosed, Dr. Bartholomew points out: “Doctors don’t know about lipedema — it’s that simple.”
Advertisement
Yet there are many telltale symptoms, including:
“Most doctors think obesity, heart failure, kidney failure, liver disease, thyroid problems or medications cause the leg swelling,” Dr. Bartholomew says. “Or they think it’s lymphedema, which is swelling that usually occurs in one arm or leg.”
While lipedema and lymphedema both do involve swelling, that’s where their similarities end.
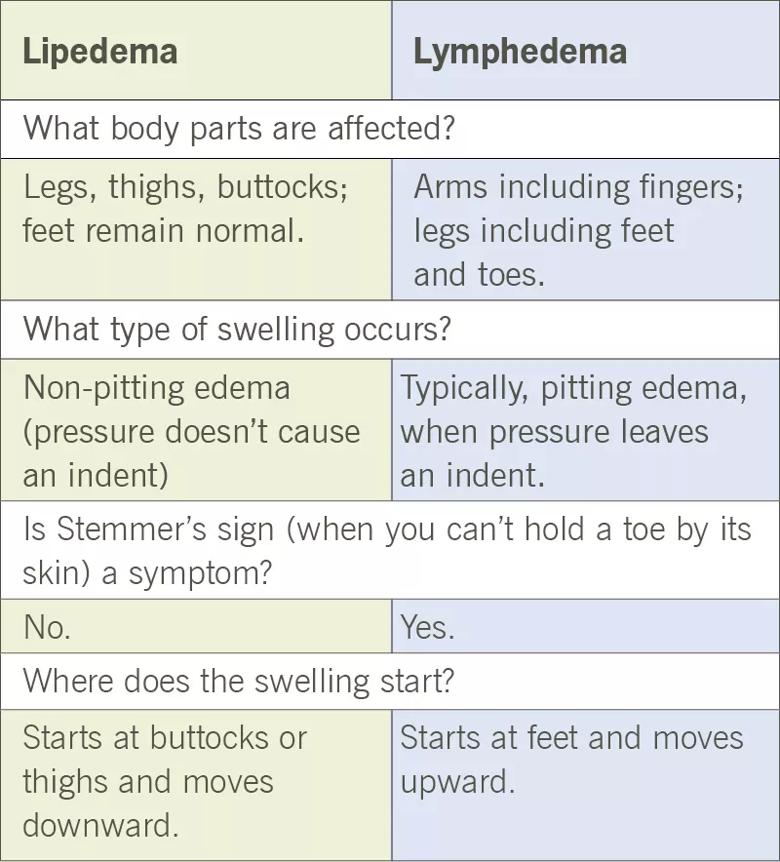
Lymphedema treatments won’t help someone with lipedema, so a correct diagnosis is crucial. Some patients with lipedema develop secondary lymphedema (referred to as lipo-lymphedema), where fat growth interferes with the lymphatic system. Lymphedema treatments may help some of the symptoms, but it still won’t resolve the lipedema.
While there are no proven medications for lipedema, Dr. Bartholomew says there are some lifestyle changes and treatments that can help:
Dr. Bartholomew also emphasizes that finding emotional support can be huge — especially from other women living with lipedema. To connect with others about the condition, visit:
Lastly, try not to be intimidated by a dismissive doctor. Chances are, the doctor simply doesn’t know what lipedema is.
In those cases, he encourages women to give information about lipedema to their physician. “If you have a physician who is understanding and will look at it, then stay with that physician,” he recommends. “If they tell you, ‘No. You’re just fat and not following your diet,’ get a different doctor.”
Advertisement
Advertisement
Learn more about our editorial process.
Advertisement

Moderation is best when consuming caffeinated drinks to avoid unhealthy spikes in BP

Medications, dietary changes, abdominal massage and physical activity can all help you start to feel better

No, you can’t prevent pregnancy by douching after sex, having sex standing up or having sex only at the ‘safe’ time

Things like stress, heated styling and other health conditions may cause you to lose more hair than normal

Having atrial fibrillation increases your risk of stroke — but blood thinners can help for many people

A high intake of sugar can cause an increase in ‘bad’ cholesterol and a decrease in ‘good’ cholesterol

A second appointment is common, especially after your first mammogram and if you have dense breasts — but it doesn’t necessarily mean anything is wrong

Living with this rare cardiac condition is easier than it used to be, thanks to new treatments, clinical trials and a strong support network

If you’re feeling short of breath, sleep can be tough — propping yourself up or sleeping on your side may help

If you fear the unknown or find yourself needing reassurance often, you may identify with this attachment style

If you’re looking to boost your gut health, it’s better to get fiber from whole foods