Sunscreen alone may not be enough to protect photosensitive skin
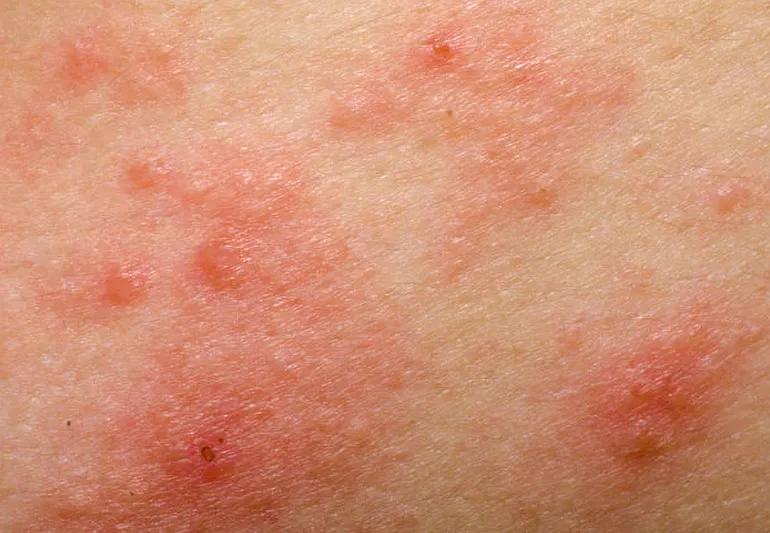
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/7aa0ab4c-cfda-45a4-ba99-cba484b8dab5/phtotoxicitySkinRash-prevOnline-770x533-1_jpg)
phototxicity skin rash
Does your skin have an extreme reaction when you spend time in sunlight or artificial ultraviolet light? If so, it may surprise you to know that the medications you take may cause this intense sensitivity. And sunscreen is likely only part of the solution.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
“The reaction can present as exaggerated sunburn or as eczema-like red, itchy spots,” says dermatologist Anthony Fernandez, MD, PhD. “And if you think you can protect yourself by loading up on sunscreen, you should know that you’ll probably need more protection than the average person.”
Different medications (including pills and those applied to the skin or injected) cause photosensitivity for different reasons.
“For the most part, the combination of the drug and the ultraviolet light (both UVA and UVB) from the sun generates toxic and inflammatory reactions that are harmful for skin cells,” explains Dr. Fernandez.
The most common reaction, known as phototoxicity, causes a sunburn-like effect on skin when you go out in the sun. Your skin may react shortly after you go out in it or it may take up to 24 hours to show up.
The itchy rash — a photoallergy — isn’t as common. It typically appears a few days after you’re out in the sun. The rash sometimes even shows up on skin that wasn’t directly exposed.
Both prescription and over-the-counter drugs can cause a reaction, including very common ones like ibuprofen and birth control pills.
“Some of the commonly used drugs include antibiotics such as trimethoprim (Bactrim®) or ciprofloxacin and some diabetes medications (including glipizide, glyburide and glimepiride),” Dr. Fernandez says.
Advertisement
Your skin may react to other drugs, too, including:
But that’s not all! There is a wide range of medications that can cause sun sensitivity, from antifungals and cholesterol-lowering drugs to tranquilizers.
If you’re wondering whether or not photosensitivity is a side effect of a medicine you’re currently taking, you can check out the U.S. Food and Drug Administration’s (FDA) list of medications that can cause sun sensitivity.
While there are a lot of medications out there that have the potential to cause phototoxic or photoallergic reactions, whether or not they will can be hard to predict.
According to Dr. Fernandez, two people can take the same medication and one person might see a reaction, while the other doesn’t. To make things still more complicated, your skin may react every time you take the medication and go out in the sun, or it may only happen once.
“People with fair skin, blond or red hair and blue eyes are more sensitive to sunlight in general,” notes Dr. Fernandez. “However, anybody can get an exaggerated sunburn due to medications, regardless of skin color.”
“The best way to minimize these reactions is strict sun protection and avoiding excessive sun exposure,” he advises. “Even sunlight exposure through windows at home or while driving can cause a reaction.”
Sunscreen protects against some harmful rays. According to the American Academy of Dermatology Association, it is most effective if:
Avoid going out in the sun during the peak hours of intensity — between 10 a.m. and 2 p.m. And while sunscreen helps, wearing protective clothing, such as a broad-brimmed hat and long sleeves, is a better strategy to minimize the risk of drug-induced sunburns.
Check with a healthcare provider or pharmacist if you’re not sure whether the medications you take may pose a risk. And remember: Even if you’re not on any medications, you should still always protect your skin when you’re in the sun.
Advertisement

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about our editorial process.
Advertisement
Both inflammatory conditions have varying triggers and symptoms
Keeping your skin dry, wearing the right clothes and investing in anti-chafe products can help minimize skin irritation
Working with a therapist, staying active and practicing mindfulness are just a few ways to help manage stress
Laser hair removal, laser surgery, excision and steroid injections are all potential treatment options
Use products that reduce inflammation without causing irritation and avoid fragrances, dyes and exfoliators
Nutrition plays an important role in managing this chronic inflammatory skin disease
Aloe vera, warm compresses and diet adjustments can help alleviate symptoms
Popping or prodding at these cysts could lead to infection
Although it could be used as a moisturizer, this new trend is not recommended
Communicating clear limits helps protect your time, energy and emotional well-being
High cholesterol can be genetic, but testing and treatment can lower your heart disease risk