How to find a fix for the itch
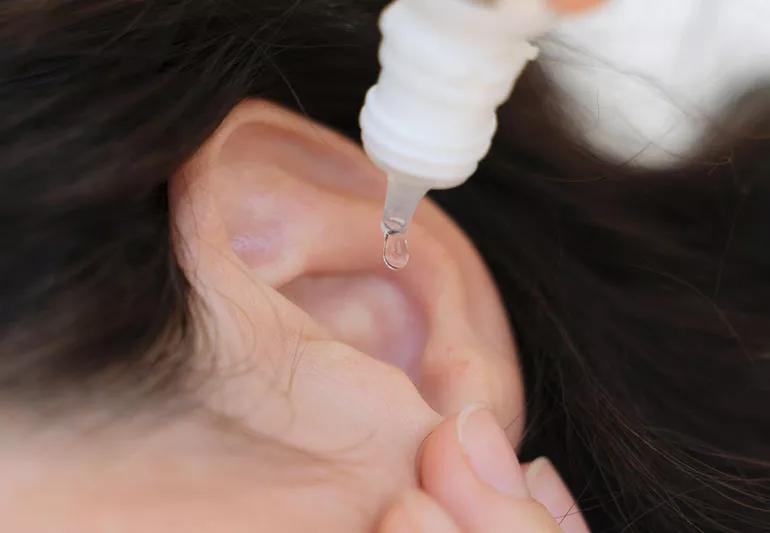
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/b32a4384-cf6b-471f-98e2-3dff472ee61e/earDrops-1270034662-770x533-1_jpg)
itchy ears and ear drops
When it comes to itchy ears, you may be your own worst enemy. So put down that cotton swab (or whatever you were about to stick in there) and think about that for a minute.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Now let’s talk about what you should — and shouldn’t — do for your ears.
Itchy ears are quite common and aren’t usually a sign of a serious condition. But sometimes, the things you do, or forget to do, can cause them to itch — or make the problem worse.
Ear surgeon Erika Woodson, MD, says itchy ears are a universal experience. “It’s part of the human condition, but it’s not generally something to be concerned about,” she says.
Dr. Woodson traces the most likely causes of these problems.
Dr. Woodson says nearly half the people she treats have ear conditions they caused themselves. The biggest culprit? Excessive or intrusive cleaning.
“The purpose of earwax is to waterproof and protect your ears,” she explains. “It has both antifungal and antibacterial properties to help prevent infection.”
Over-cleaning can remove that protection. While it may provide temporary relief, it leaves you open to bigger problems than that tickle in your ear.
Sticking objects in your ear canal to clean it (or to scratch an itch) often just makes matters worse. You’ll likely just push the wax farther in. With time, that can lead to earwax buildup.
Itchiness is often a symptom of wax buildup, but you’ll likely notice other signs — pain or an odor coming from your ear, for instance.
Advertisement
“Most of us don’t need to clean our ears at all,” says Dr. Woodson. Earwax generally comes out of your ear canal on its own. And you can wash it away from your outer ear when you bathe.
You can typically treat earwax buildup at home. Use ear drops to break up the wax. After you shower or take a bath, just pat the external ear canal dry with a towel. Don’t try to clean out your ear canal with anything else, Dr. Woodson advises. See your doctor if drops aren’t effective.
Dermatologic conditions like eczema and psoriasis can surface on various areas of the skin — and make you itch.
But the rashes or plaques can also develop in places your eye can’t see.
“Your ear canal is lined with skin like the rest of your body, so eczema and psoriasis may also show up there,” Dr. Woodson explains.
If your ears itch and you have a condition like eczema or psoriasis, see your dermatologist, or an ear, nose and throat (ENT) specialist. “Get your ears checked out — your itch may be caused by a treatable dermatologic condition,” says Dr. Woodson.
Itchiness is one early symptom of an ear infection. But you’ll typically see other symptoms as well.
“If you feel pain in the ear or there’s discharge from the ear, it’s time to call your doctor,” Dr. Woodson advises.
These are signs of an infection, which can harm your ears or damage your hearing.
Dr. Woodson notes that those who use hearing aids or earbuds are sometimes more prone to fungal ear infections.
Don’t hesitate to call your doctor about an ear infection. And if you wear a hearing aid or earbuds, clean them regularly to avoid itchiness and infection, following the manufacturer’s directions.
Yes, food allergies can cause your ears to itch. For those with hay fever or a pollen allergy, your ears may begin to itch after you eat foods like nuts, soy, wheat, milk, fish and shellfish.
If you have a pollen allergy, known as oral allergy syndrome, you may feel itching in your ears after eating foods like apples, melons, bananas, cherries, kiwis, sunflower seeds, hazelnuts and almonds.
You may develop hives and have itching on other areas of your face, too. If you’re having trouble breathing after eating any of these foods, you may be experiencing anaphylaxis and should seek treatment immediately.
You may have a sensitivity to certain metals like nickel that are used to make jewelry, including earrings. Wearing earrings may lead to itchy ears.
Nickel is one of the most common skin allergies. If you’re allergic to nickel, you may experience itchiness, redness, dry patches or even swelling. Symptoms typically last 12 to 48 hours after contact.
Advertisement
The best treatment is to avoid contact with nickel, but if you have mild symptoms, over-the-counter hydrocortisone cream and antihistamines can help.
Mild ear itchiness is usually temporary and goes away on its own. If your itch lasts more than a few days, or if you have other symptoms, see your doctor. And remember, cleaning your ears the right way will help you avoid problems.
Advertisement

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about our editorial process.
Advertisement
You can find sweet relief by swallowing, yawning and doing specialized maneuvers
Yes, ear pain can result from seasonal allergies, causing even more issues
Turning your head to the side and pulling your ear up and back is one common tactic for relief
Ear plugs, bathing caps, hydrogen peroxide and hair dryers can all help keep ears clean and dry
Not all ear infections need antibiotics — cold and warm compresses and changing up your sleep position can help
Ear infections can be painful, but essential oils may make the problem worse
Throat and ear pain that lasts more than four weeks deserves serious attention
And two remedies to avoid at all costs
Although it could be used as a moisturizer, this new trend is not recommended
Communicating clear limits helps protect your time, energy and emotional well-being
High cholesterol can be genetic, but testing and treatment can lower your heart disease risk