It starts off like a cold and then progresses to a rash that can last about 10 days
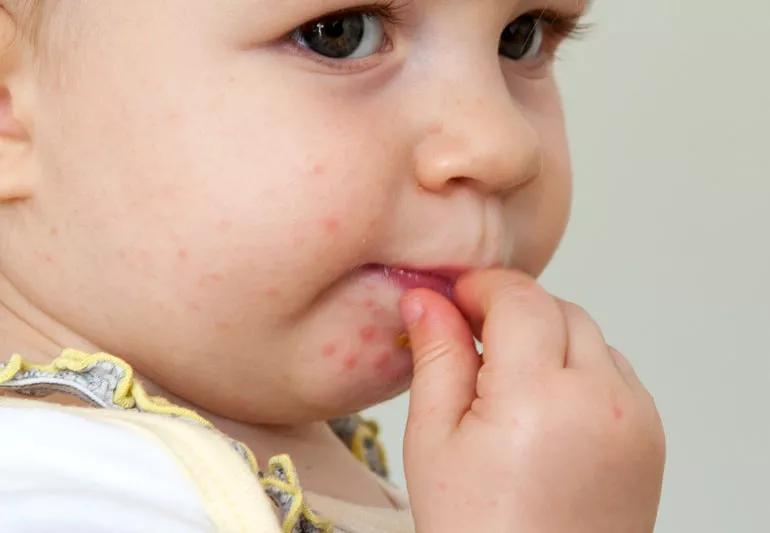
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/efe09d9e-4330-4244-bca0-5703ebd63cb8/childHFMD-182093379-770x533-1_jpg)
Child with hand foot and mouth disease
Your child is cranky, running a fever and going through tissues like there’s no tomorrow.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Then, they won’t eat.
Then, you see a rash. And their best friend’s mom from daycare calls and says her child hasn’t been feeling well either.
And now it’s all making sense.
It might be hand, foot and mouth disease, a common but highly contagious childhood illness that makes its way — very quickly — through households, daycares and schools.
“Like most viruses, hand, foot and mouth is fairly contagious,” says pediatrician Dana Schmidt, MD. “So, in a daycare or school setting, it can spread very quickly.”
Caused by a strain of the coxsackievirus, hand, foot and mouth disease is best known for the blister-like rash that appears on the — you guessed it — hands, feet and mouth. Contrary to its name, though, the rash can appear all over the body.
Dr. Schmidt answers your most pressing questions about this common and highly contagious illness.
A: Hand, foot and mouth disease will initially look similar to a cold. After a few days, a rash will start to form.
The first symptoms of hand, foot and mouth disease are similar to a cold and include:
It’s during this first phase of the disease that you’re most contagious and most likely to pass the virus to other people, Dr. Schmidt says.
Advertisement
After the initial symptoms set in, you may notice small sores inside of your mouth, including on your gums, tongue and roof of your mouth. The spots may appear like small red bumps or larger open sores.
These sores can make swallowing painful, so it’s common for people with hand, foot and mouth disease to not want to eat. It’s also common that mouth sores will cause children to drool.
Sometimes, the rash stops at the mouth. That’s called herpangina (and the advice below still applies).
In the next day, you may notice sores spread to the hands and feet, and possibly elsewhere.
“The hallmarks of the virus are a rash that appears on the hands, feet and mouth, but the rash can often be found all over the body, including the trunk and genitals,” Dr. Schmidt states.
The look of the rash can vary from person to person. Some people experience small, red spots that don’t cause any discomfort. Others may have larger spots, sometimes filled with pus, that may be painful. The spots may contain the virus, so avoid touching the rash as much as possible, and wash your hands thoroughly after coming in contact with blisters. The rash usually isn’t itchy.
The spots should clear up in about 10 days.
A: You’re most contagious with hand, foot and mouth disease during the first few days of being sick —often before blisters appear. Once the blisters dry up, you’re less likely to pass on the virus, though it can live in your stool for weeks after the rash clears.
Hand, foot and mouth disease can be spread in several ways:
If your child becomes infected, prevent the spread by keeping them home from daycare, school or other group activities. If you’re infected, stay home from work or school.
A: Yes. Hand, foot and mouth disease is very common and usually affects infants and children under the age of 5. But because it’s so infectious, it can spread among family members and daycare providers. It can make older kids, teenagers and adults sick.
A: Yes. Dr. Schmidt explains that because multiple viruses can cause hand, foot and mouth disease, it’s possible to catch the virus multiple times.
You can do several things to prevent or reduce the spread of hand, foot and mouth disease:
Advertisement
Hand, foot and mouth disease has no specific treatment, although the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reports that most people get better on their own within seven to 10 days. But you can treat symptoms of the virus with over-the-counter pain medications.
It’s also important to stay hydrated. Because mouth sores can make eating and drinking uncomfortable, dehydration is a common side effect. Avoid foods and drinks that are acidic, like orange juice, as they can irritate mouth sores. Stick to milder or cold foods. Older children and adults may also relieve some discomfort with salt water gargles, although this treatment isn’t recommended for infants, toddlers or younger children.
Be especially vigilant if hand, foot and mouth disease symptoms become severe, or if you or your child has a weak immune system or becomes dehydrated. Talk with a healthcare provider if the fever doesn’t go away after three days or if all symptoms don’t improve after 10 days.
Advertisement

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about our editorial process.
Advertisement
Yes, but symptoms can be easy to miss
You can catch this highly contagious virus through contaminated food, water, droplets and more
Use a bleach solution to sanitize surfaces like doorknobs, counters, toilets and light switches
Start slowly with clear fluids, and then move to bland, easy-to-digest foods
Transmission typically involves skin-to-skin contact, but the virus can also linger on surfaces
Time of onset and duration of symptoms tell the story
It’s not just smoking and genetics that can increase your risk of cancer
Mpox (monkeypox) is transmitted through skin-to-skin contact, including sex
Prioritize your health by managing stress, strengthening your social connections and getting quality sleep
Bolsters, blankets, pillows and blocks can offer extra support, stability and comfort
Allergies, postnasal drip, asthma or reflux could be to blame for a cough that won’t quit