Advertisement
Test your knowledge about this ancient medical art
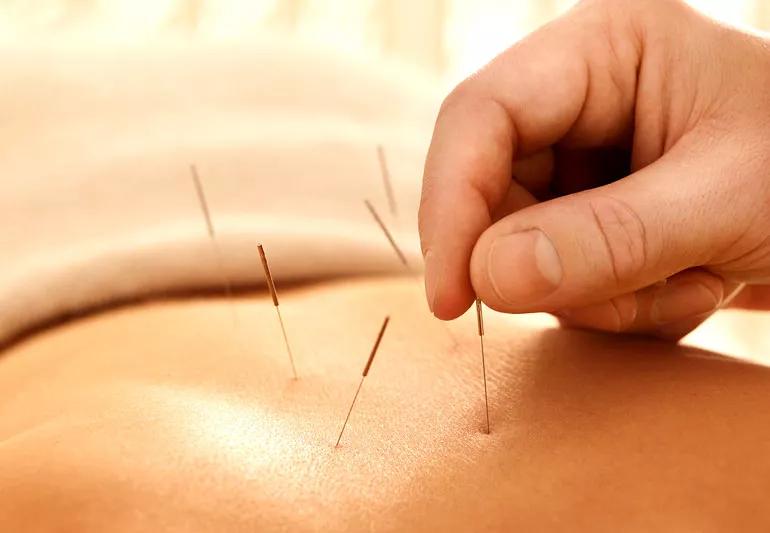
Acupuncture is a timeless form of medicine that originated in China and has been around for thousands of years. But you may have been afraid to try it despite its many health benefits because of the thought of needles.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Over the last few years, acupuncture has seen a rise in popularity among healthcare providers as a viable form of treatment — one that can help treat conditions like chronic back pain, headaches, nausea after chemotherapy among many others.
“Acupuncture is ancient. But it’s an ancient medicine that has a place in modern healthcare,” says licensed acupuncturist Megan Scott, LAc. She says acupuncture has withstood the test of time as one tool in the treatment toolbox that can help improve quality of life.
“There are a lot of misconceptions about acupuncture, but the truth is that this practice has been around for more than 3,500 years and provides relief to people around the world,” says Scott.
Below, find the most common myths about acupuncture
Perhaps the thought of being poked by several needles at once sends a shiver up your spine. It’s a common reaction. But it doesn’t have to be. That’s because there’s very minimal discomfort with acupuncture because the needles used are so fine and thin — about the size of a cat’s whisker.
You may or may not feel an initial prick, sometimes described as a mosquito bite. Scott shares how a patient who was new to acupuncture described it in a televised piece: “It felt like a baby was pinching me at times, but it really didn’t hurt at all.”
Advertisement
Any discomfort will either fade on its own or ease up as your acupuncturist adjusts the needles. “We can always adjust needle sizes because certain people need lighter touch.”
But Scott says “Our goal is to make treatment as comfortable as possible.”
“Patients get in a comfortable position on the exam table, and then we insert the needles,” says Scott. “Most of the time, patients don’t even notice that they’re there.
She says a lot of her patients are surprised that they rest — and even fall asleep — with needles in.
It’s true that acupuncture is ancient. But it’s a treatment option that many medical institutions recommend. Even the United States military uses acupuncture. There are many clinical research trials on acupuncture. Both the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and the World Health Organization (WHO) recognize acupuncture as a valid treatment for a wide range of conditions.
“A lot of doctors refer their patients for acupuncture now,” says Scott, adding that insurances are now covering it for a myriad of purposes.
Acupuncture is used by a diverse patient population, from very young to very old. Scott says sometimes geriatric and elderly patients find acupuncture because they’re looking for something that has less risks than traditional approaches to pain management.
“Acupuncture can be performed alongside most all conventional therapeutics, with a few exceptions,” says Scott. “Your acupuncturist will evaluate the process so acupuncture is synergistic and complements other treatments to support better health outcomes overall,” she adds.
She does offer caution if you’re taking blood thinners, however.
“If a patient is on blood thinners, we just use smaller needles. And there might be a very minor increased risk for bruising and bleeding,” she clarifies.
It’s true that acupuncture can help relieve pain. But it’s also used for a wide range of treatments for other health issues, including:
Acupuncture has few to no side effects.
“After your acupuncture session, you can usually carry on with your day without any restrictions,” says Scott.
The response to acupuncture is always an individual one. Some people with acute and minor issues respond quickly — within one, two or three treatments. Others need a course of eight to 10 treatments to see notable improvement. Acupuncture’s effects are cumulative, building with each treatment.
Advertisement
But Scott clarifies: “People think that acupuncture is a one-stop shop, which it is not for the majority of complaints that we see. It’s more of a process, not one treatment.”
Scott clarifies further: “Once we’ve reached goals with resolution or management of a condition, we’re able to wean you from treatment. Our goal is always to get you as independent from the treatment while enjoying sustained benefit. That could be no follow up necessary for one person and follow up every couple of weeks or monthly for others with chronic conditions.”
Scott says for most patients, a doctor’s referral isn’t necessary, “but a lot of people do learn about acupuncture from their doctor.” She says sometimes patients find their way to acupuncture through word-of-mouth.
Guidelines vary by state. In Ohio, for example, you don’t need a doctor’s referral or prescription for acupuncture, but a physician should perform a diagnostic exam for the condition you plan to treat. It’s important you seek out a qualified and licensed acupuncturist before starting any course of treatment.
Advertisement
Learn more about our editorial process.
Advertisement

It’s great for stress relief, which can go a long way when you’re trying to conceive
This ancient treatment is often a complement to acupuncture
Discover the benefits of this ear acupuncture technique

Find out what it is and how it can help the body heal
Acupuncture, herbs and hypnotherapy curb cravings naturally
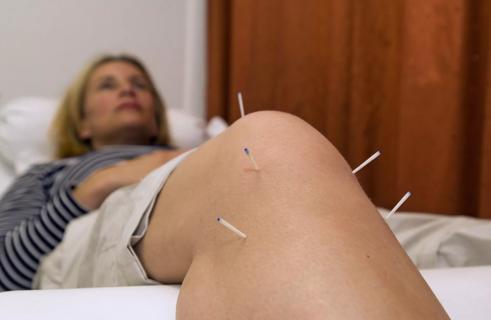
Traditional Chinese medicine technique recommended for chronic pain
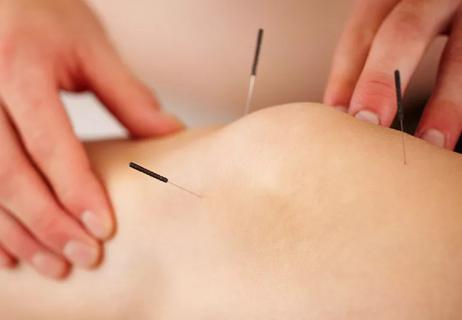
New government advisory recommends non-addictive options first

Somatic Pilates is less form-focused and more experience-focused

If you’re feeling short of breath, sleep can be tough — propping yourself up or sleeping on your side may help

If you fear the unknown or find yourself needing reassurance often, you may identify with this attachment style

If you’re looking to boost your gut health, it’s better to get fiber from whole foods