Typical signs include growth delays and low energy
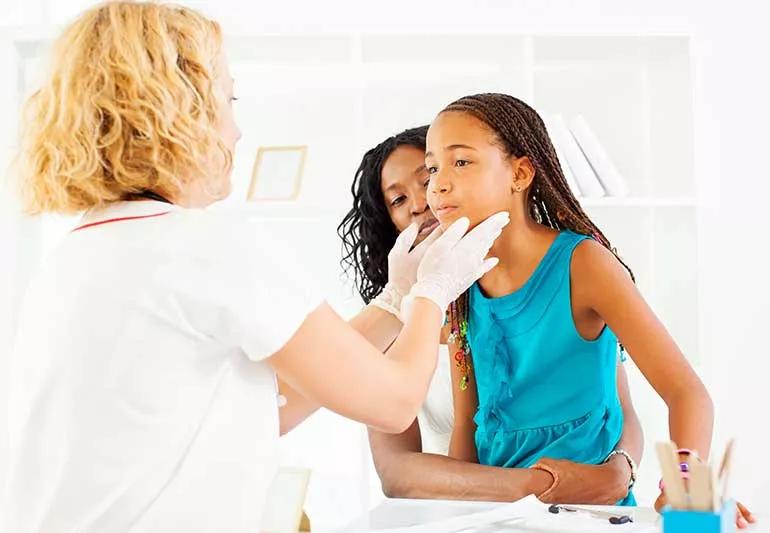

As parents, we tend to be vigilant about our kids and their development. We’re on the lookout for cues they’re getting enough sleep. That they’re getting the vitamins and minerals they need. That they develop appropriate coping skills.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
So, if your child is shorter than friends their age and doesn’t seem to match their energy level, you notice. And you may worry. Because you know those can be signs of an underactive thyroid — or childhood hypothyroidism.
Luckily, hypothyroidism in kids can be easy to diagnose, and treatment is highly effective.
We talked with pediatric endocrinologist Roy Kim, MD, MPH, about symptoms and treatment so you can know what to look for and what to expect so you can take the best care of your kiddo.
When their thyroid isn’t functioning at full speed, it can slow things down all across your child’s body. That may include both physical delays and behavioral symptoms.
Some symptoms may include:
“Parents who recognize symptoms of childhood hypothyroidism in their kid should see their child’s healthcare provider, who can order thyroid tests or other tests,” Dr. Kim recommends. “If the pediatrician suspects or finds a thyroid condition, you should be referred to a pediatric endocrinologist.”
Advertisement
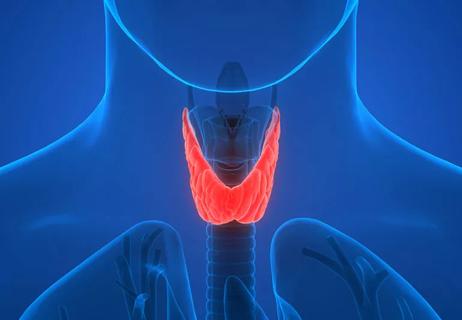
Your thyroid is a butterfly-shaped gland at the base of your neck. It produces hormones that are critical for kids’ growth and development. Your thyroid is essentially what controls the speed of your metabolism (also called your metabolic rate). So, it controls how quickly (or slowly) you transform food into fuel that energizes your whole body.
When your thyroid releases too many hormones, your metabolism speeds up. That’s called hyperthyroidism.
When it releases too few hormones, your metabolism slows. That’s hypothyroidism.
Hypothyroidism — also called low thyroid — can be something a child is born with (congenital), or it may develop later (acquired).
Congenital hypothyroidism affects about 1 in 4,000 newborns. Babies with congenital hypothyroidism may have a thyroid gland that’s underdeveloped, missing or in the wrong place. Or it may be structurally sound, but for other reasons, doesn’t secrete hormones the way it should.
Congenital hypothyroidism can often be identified during routine newborn screenings at the hospital. And early treatment can prevent delays in their growth and behavior.
“Newborns with congenital hypothyroidism can look perfectly healthy and happy,” Dr. Kim explains. “If not treated from infancy, you probably will begin to notice symptoms as they’re found to grow poorly or have developmental delays.” In other words, children with congenital hypothyroidism may begin sitting, walking, talking or understanding words later than expected.
In severe cases, babies with hypothyroidism who aren’t properly treated may not eat well. They also may have prolonged jaundice (yellowing of their skin) or poor muscle tone.
More common than congenital hypothyroidism is acquired hypothyroidism. Children with acquired hypothyroidism are born with a fully functioning thyroid, but the gland stops working properly as they grow.
Often, acquired hypothyroidism is a result of Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. It’s an autoimmune disease where your child’s immune system mistakes cells in their thyroid gland as a threat. Their immune system attacks their thyroid gland and weakens it, causing it to not produce the hormones your child needs for proper development.
Hashimoto’s affects up to 1 in 100 children.
“Hashimoto’s thyroiditis can cause slow growth in children,” Dr. Kim notes. “Its other symptoms include things like constipation, low energy, feeling cold, dry skin and high cholesterol. They’re similar to the symptoms you see in adults with hypothyroidism.”
Acquired hypothyroidism tends to run in families. So, to help diagnose acquired hypothyroidism, your child’s healthcare provider will take a family history to better understand their risk for the condition. Their provider will also do an exam to feel for an enlarged thyroid. Blood tests — called TSH (thyroid stimulating hormone) tests — can check for signs of how well their thyroid is functioning.
Advertisement
Hypothyroidism typically doesn’t go away. But treatment can successfully manage symptoms.
Kids with acquired or congenital hypothyroidism are treated the same way as adults. Typical treatment uses a synthetic thyroid hormone. That replaces the natural hormone their thyroid can’t make.
Levothyroxine is the most common medication used for hypothyroidism. It also goes by the brand names Synthroid®, Levoxyl® and Unithroid®.
“Levothyroxine works extremely well in children,” affirms Dr. Kim. “It keeps their growth normal, and it keeps their puberty on track.”
But Dr. Kim stresses that replacing thyroid hormone only helps when the gland is underactive: “Plenty of kids can have constipation, dry skin or irregular periods that may be due to causes not related to the thyroid.” So proper testing and diagnosis is important.
Regular tests to check thyroid hormone levels are critical for children taking medication for hypothyroidism. One reason for that is to ensure the dosage of the medication is appropriate for them.
Medication in too high of a dose can lead to hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid). Children with hyperthyroidism may become hyperactive and unable to sit still. And they could have trouble sleeping or display impulsive behavior.
Advertisement
Your child’s healthcare provider can make sure their treatment is providing just the right amount of hormones for their optimal development. Not too little. Not too much. Just right.
“If your child needs treatment, work with your pediatric endocrinologist,” Dr. Kim advises. “Take the medicine very consistently, and get follow-up blood tests regularly.”
Advertisement
Learn more about our editorial process.
Advertisement

Hypothyroidism is underactivity of your thyroid gland, while hyperthyroidism is overactivity — but both conditions need treatment

No diet can cure hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism, but some foods and supplements can cause trouble

Foods high in selenium, like Brazil nuts, cottage cheese and some fish, can help support healthy thyroid function

Only take supplements recommended by your healthcare provider — others can worsen your condition

Hyperthyroidism can make you feel sluggish and exhausted — but so can other conditions
The truth about natural thyroid symptom relief
How overtreatment for hypothyroidism places you at risk

Wearing a scarf, adjusting your outdoor activities and following your asthma treatment plan can help limit breathing problems

Your diet in the weeks, days and hours ahead of your race can power you to the finish line

When someone guilt trips you, they’re using emotionally manipulative behavior to try to get you to act a certain way