It’s 97% effective in preventing shingles in people between the ages of 50 and 69
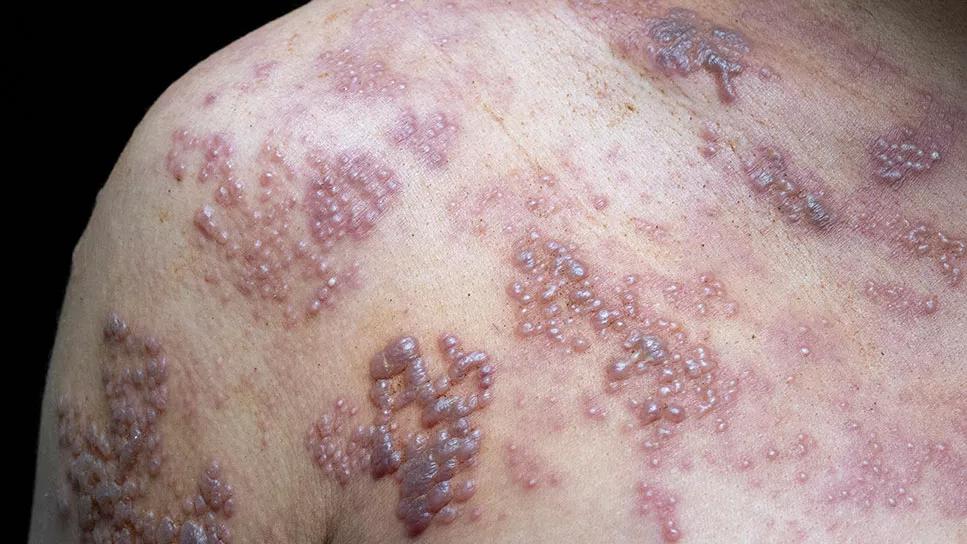
No one likes to get shots, especially for something you’ve already been vaccinated for. But the new(ish) version of the shingles vaccine is worth offering up your arm for.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
If you were vaccinated against shingles before 2020, you received Zostavax®. Post-2020, there’s a new two-dose vaccine on the scene called Shingrix® — and it’s so much more effective that you can’t actually get Zostavax in the U.S. anymore. Shingrix is officially the only game in town. And the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) wants people who received Zostavax to make the switch.
When we say Shingrix is the better vaccine, we’re serious. It’s more than 90% effective at helping prevent shingles, compared to Zostavax’s 50% effectiveness. And Shingrix remains above 85% effectiveness in people over the age of 70.
The news is all good, but that doesn’t mean you won’t have questions. So, we asked family medicine doctor Matthew Goldman, MD, to tell us a bit more about Shingrix and shingles and how chickenpox fits into the conversation.
Anybody who’s had chickenpox can get shingles. In the U.S., approximately 99% of people over the age of 40 fit that particular bill. Researchers can’t say for sure why the chickenpox virus reanimates in 10% of us, zombie style, but it seems shingles is most likely to crop up when we’re under stress.
We also know that some people run a higher risk of ending up in the unlucky 10% than others, like:
Advertisement
And in case you’re wondering: No — people who haven’t had chickenpox can’t get shingles. But they can get chickenpox from a person with shingles. It’s the world’s itchiest consolation prize. And, of course, once you’ve had chickenpox, the virus that causes shingles stays with you.
Yup! The shingles vaccine is the only way you can reduce your risk of getting shingles. We don’t know what causes the chickenpox virus to reactivate, so we don’t have other prevention options.
It’s also important to keep in mind that Shingrix is the only way to protect yourself against common shingles complications, like postherpetic neuralgia (PHN).
So, who should get the vaccine? The CDC recommends the vaccine for all adults ages 50 and older, regardless of whether they’ve had shingles before. They also recommend the jab for people over 19 years old with weakened immune systems due to disease or therapy.
Dr. Goldman explains that the standard recommendation for Shingrix is a two-dose series, with the second dose administered between two and six months after the first.
We live in interesting times. The United States has been vaccinating children against the virus that causes chickenpox for about a quarter of a century now. That means people born in the U.S. after 1995 have a decent chance of living their whole lives without ever experiencing chickenpox — which, as we’ve discussed, is a prerequisite for shingles.
Of course, there are always exceptions that prove the rule.
“Some people do get shingles after they received the chickenpox vaccine,” Dr. Goldman notes, “but it’s rare, and the risk is lower compared to people who had a natural chickenpox infection. In other words, you’re far more likely to get shingles after having chickenpox, which is why it’s important to get vaccinated.”
Thanks to the COVID-19 pandemic, people are more open than ever to wearing masks. Especially during respiratory season, it’s the right thing to do for your loved ones, friends and neighbors. But in the case of shingles, it’s not going to do much good.
That’s because shingles isn’t a virus: It’s a condition caused by a virus. You can’t spread it to other people. What you can spread is the virus that causes shingles: chickenpox. It’s highly unusual — but not completely impossible — to transmit varicella-zoster through respiratory droplets.
Advertisement
“You’re far more likely to pass the virus on through the fluid that oozes from your blisters,” Dr. Goldman explains. If your rash has reached the blister phase, you should keep it covered and stay away from anybody who hasn’t had either chickenpox or the chickenpox vaccine. To be extra safe, avoid contact with immunocompromised people until your rash is gone, too.
We hate to burst your bubble, but contrary to popular belief, you actually can have multiple episodes of shingles. If you’re unlucky enough to fall into that category, Dr. Goldman says you can expect the rash to appear on a different part of your body the second (or third) time around than it did in the past.
It’s like a law of nature: We tend to be most enthusiastic about preventive medicine once we’re sick. And vaccines are no exception.
Hindsight may be 20/20, but it’s still hindsight. If you have an active case of shingles, you can’t get vaccinated. Shingrix won’t do anything to help if you’re already sick. It’s preventive, not therapeutic, which means it exists to help prevent you from getting sick or — if you have a breakthrough case — to reduce your chances of experiencing complications.
“You have to wait until the rash has healed completely,” Dr. Goldman states. “But you absolutely should get the Shingrix vaccine once you’re well again. It can help prevent a shingles recurrence, which nobody wants.”
Advertisement
Your risk of shingles and PHN increases as you get older. And unlike some vaccines, Shingrix doesn’t protect you for life. That’s why it’s important to keep track of your vaccination records and, if necessary, get boosters.
Dr. Goldman explains that there isn’t a one-size-fits-all recommended approach for booster shots. Whether or not you need a booster (or several) depends on your individual circumstances.
“I’d advise talking to your primary care provider,” Dr. Goldman recommends. “They can look at your personal health history and the things that are going on in your life to determine how often you need a booster.”
Research suggests that over 85% of people ages 70 years and older remained protected from shingles for at least four years post-Shingrix, but your health status and other risk factors may require a slight adjustment to your vaccination schedule.
The Shingrix series is nearly twice as effective at preventing shingles and complications like PHN. For that reason, the CDC strongly encourages Zostavax recipients to roll up their sleeves once again. The same goes for people over 50 who’ve already had shingles and/or received the chickenpox vaccine. If you have any questions about your eligibility, talk to your healthcare provider.
Advertisement
Learn more about our editorial process.
Advertisement

If you have a weakened immune system, your risk for getting shingles a second or third time increases
But if you haven’t been vaccinated, you could get chickenpox from somebody with shingles

From influenza and COVID-19 to pneumococcal, shingles and more, vaccines help keep you healthy

Most routine vaccines are safe for people living with multiple sclerosis — but be sure to talk with your care team about your needs
Postherpetic neuralgia is challenging, but help is available
Shingrix vaccine for compromised immune systems

Chemo cold caps may help you keep more of your hair during therapy

Fainting, heart palpitations and shortness of breath are just a few signs your heart may need help

If you’re feeling short of breath, sleep can be tough — propping yourself up or sleeping on your side may help

If you fear the unknown or find yourself needing reassurance often, you may identify with this attachment style

If you’re looking to boost your gut health, it’s better to get fiber from whole foods