Advertisement
Adult vaccination has begun, while clinical trials for a children's vaccine are underway
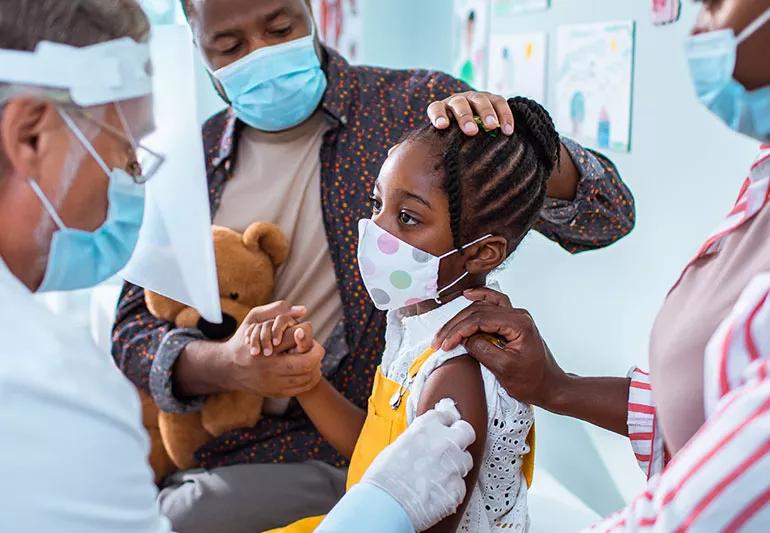
The United States finally has a coronavirus vaccine for adults (three to be exact!). And although this is fantastic news, experts say that children will also need to be vaccinated to get the pandemic under control. Still, clinical trials for a kid’s vaccine are underway, and although it may take another year to receive the data and produce a vaccine, it’s promising news.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Pediatric infectious disease specialist Frank Esper, MD, explains the ins and outs of developing a vaccine for children and why the first COVID-19 vaccines weren’t approved for kids.
“Both adults and children will need to be vaccinated for things to return to some sort of normalcy,” explains Dr. Esper. “Many vaccine manufacturers have now started research and clinical trials for a vaccine that is safe and effective for kids.”
Kids weren’t involved in the original adult clinical trials because the data tells us that severe illness from COVID-19 tends to happen to adults (especially in older adults). We’re not seeing the same sort of response or sickness in children.
That’s not to say that children are immune to COVID-19, because they aren’t. But they tend to be more resilient and fare better if they get sick, notes Dr. Esper (although a very small number of kids have developed a serious inflammatory condition linked to coronavirus).
One of the reasons for focusing on an adult version first is because when children are involved in clinical trials, there is oftentimes more layers of protection to go through. For instance, the child and both parents typically have to agree to participate in the trial or study.
Advertisement
“Kids are a special and vulnerable population and we try to protect them because they can’t make decisions for themselves,” says Dr. Esper. “In clinical trials – whether for a vaccine or any type of treatment – we don’t want to speed things up because it’s a matter of protection and safety.”
So the first priority was for an adult vaccine, not only because of the outcomes we’re seeing, but because an adult vaccine was faster to create due to the potential risk and rigorous safety precautions needed for the development of a children’s vaccine.
“It’s encouraging to see drug companies expand their vaccine clinical trials to include babies and young children,” says Dr. Esper. “This is a crucial step in our efforts to slow the spread of COVID-19 and move closer towards normalcy.”
Here’s where current pediatric vaccine trials stand:
Since a child’s immune system is different from an adult’s, COVID-19 vaccines for younger children, especially, may require different dosage levels or formulations than the adult versions.
Immune systems in kids can vary greatly depending on age. A 16-year-old is going to have a much different immune system than a 16-month-old. Because of this, additional data and research is needed when evaluating a vaccine for kids.
It’s even true for the flu shot. Babies six months and older should get a flu shot every year, but some kids six months through eight years of age may need two doses for more protection. This is because of differing immune system responses at different ages.
“Children’s immune systems are growing up just as they are,” explains Dr. Esper. “We often split kids up by age groups and stages. We can’t just say all kid’s immune systems are the same at any given age.”
For adults, we’re often lumped together from age 18 to 65 and then 65 and over. With children, there is a much wider range in terms of stages and ages because they are still growing and developing. All of this has to be taken into consideration with a vaccine since kids at varying ages will likely respond differently.
Because of all the challenges with kid’s immune systems and the protection and safety protocols in clinical trials, a COVID-19 vaccine for children will still take some time to develop. However, these pediatric vaccine trials will provide critical safety data and help us better understand the vaccine’s immune response in children.
Advertisement
Until we have a kid’s vaccine, we must remember to follow the safety precautions we’re all now familiar with. This means wearing face masks, washing our hands, avoiding crowds and maintaining physical space from others.
Advertisement
Learn more about our editorial process.
Advertisement

Children as young as 6 months should get vaccinated, but dosage guidelines depend on kids’ ages and past vaccines

Updated vaccinations are recommended to better protect against the evolving virus

Redness, swelling, itching and rash can happen when your body’s immune system reacts to the vaccine injection
The latest vaccine offers the most up-to-date protection
Irregularities in cycle length and flow aren’t a cause for concern

Before you panic, here are the options to consider

Our expert explains why swollen lymph nodes happen

And why you shouldn't be so quick to post your COVID-19 vaccine card on social media

If you’re feeling short of breath, sleep can be tough — propping yourself up or sleeping on your side may help

If you fear the unknown or find yourself needing reassurance often, you may identify with this attachment style

If you’re looking to boost your gut health, it’s better to get fiber from whole foods