Organ meat is packed with nutrients, but it’s not good for everyone
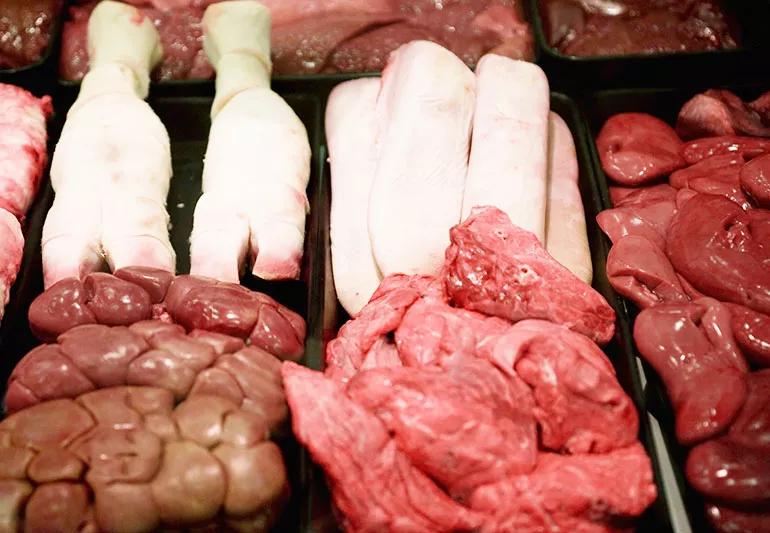
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/a7e9252d-eb55-4b09-b3c8-821f4f44f85f/Organ-Meat-85633221-770x533-1_jpg)
Vendor refrigerator of organ meat.
“What am I, chopped liver?” Somehow, being compared to chopped liver implies you’re less desirable. How did liver get such a bad rap? Chopped liver — and other organ meat (also called offal or variety meats) — is packed with nutrients and bursting with flavor. (Don’t knock chopped liver smothered in fried onions till you’ve tried it!)
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
“Organ meat is loaded with health benefits, more so than the muscle meat we typically prefer,” notes dietitian Julia Zumpano, RD, LD. “For most people, they’re a nutritious addition to the diet when eaten in moderation.” Zumpano weighs in on the benefits of eating organ meat, along with a few precautions about who should avoid them altogether.
Organ meat is the internal organs and other parts of the animal besides muscle meat, including:
In the U.S., common organ-meat foods include:
Besides being more affordable than premium cuts of meat, organ meat is often higher in nutrients, too. The amounts of vitamins and minerals depend on the organ and the animal. But in general, you can expect organ meat to be a good source of nutrients.
Advertisement
Iron is necessary to make hemoglobin, a protein that carries oxygen throughout your body. Meat and fish contain heme iron, the easiest form for your body to use.
“If you’re looking to boost your iron intake, organ meat can potentially be one option,” says Zumpano. “Ounce for ounce, it provides more iron than other types of meat.”
For example, compare 4 ounces of chicken liver to the same amount of beef tenderloin, as measured by the U.S. Department of Agriculture’s FoodData Central:
Organ meat is rich in B vitamins, especially B6 and B12, which serve multiple important functions in your body. B6 is crucial for breaking down proteins, carbohydrates and fats. It also supports healthy immune function. B12 is necessary for making brain and nerve cells, DNA and red blood cells.
Protein is the building block of cells. It builds new cells and repairs existing ones. Although not as high in protein as traditional muscle meat, many organ meats are still a good source of protein.
For instance, the U.S. Department of Agriculture’s FoodData Central reports that 100 grams (roughly 3.5 ounces) of beef liver contains 20.4 grams of protein, while the same amount of top loin steak has 22.8 grams.
It doesn’t get a lot of attention, but alpha-lipoic acid (ALA) has been shown to have health benefits.
It protects mitochondria — the part of your cell that produces energy — from damage, and helps turn nutrients into energy. Research indicates it can be helpful for neuropathy (or nerve damage) associated with diabetes.
Your body makes alpha-lipoic acid. However, production decreases as you age. You can find the nutrient in foods like spinach, tomatoes, broccoli and organ meat (beef hearts and kidneys contain the most).
Organ meat provides many essential minerals, including:
Vitamins A, D, E and K are fat-soluble vitamins. They get absorbed along with fat and stored in fatty tissue, unlike water-soluble vitamins, which get flushed out with urine.
Organ meat is rich in fat-soluble vitamins, which contribute to vital functions in your body.
Advertisement
For the most part, yes. “Organ meat is safe for most people to eat in moderation,” says Zumpano. “But it’s high in cholesterol and saturated fat, which can increase your blood cholesterol level. If you have heart disease risk factors like high cholesterol, it’s best to choose leaner muscle meat instead.”
Those with gout (a type of arthritis) should also watch their intake of meat, including organs. They contain purines (a naturally occurring compound), which worsens gout. Children should also stick to smaller portions of organ meat than adults.
Other concerns associated with consuming organ meat include:
Advertisement
Organ meat contains more vitamins and minerals than traditional cuts of meat. Eating it can be an excellent way to get essential nutrients. But for those with certain health conditions, a high intake of organ meat can lead to problems. If you have concerns, talk to a healthcare provider or a registered dietitian. This way, you can be confident that your dinner plan — with or without a side of chopped liver — is a healthy and safe choice for you and your family.
Advertisement

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about our editorial process.
Advertisement
This color additive, found in many pre-packaged foods, may affect people with ADHD or allergies
With a focus on internal cues for hunger and fullness, this eating style may revolutionize your relationship with food
Review the ingredients, watch for sugar and fat, and choose one with the right amount of protein for your needs
Getting the hang of portions can help you better understand how much to put on your plate
A typical recommended balanced diet is half fruits and veggies, a quarter protein and a quarter grains
Foods high in protein, fiber and water can help keep hunger at bay
This quirky food trend is harmless, as long as you’re getting enough protein, fiber and healthy fats
With a little planning, you can fill your belly and boost your energy
Although it could be used as a moisturizer, this new trend is not recommended
Communicating clear limits helps protect your time, energy and emotional well-being
High cholesterol can be genetic, but testing and treatment can lower your heart disease risk