Chronic hair pulling is a behavior that requires professional help
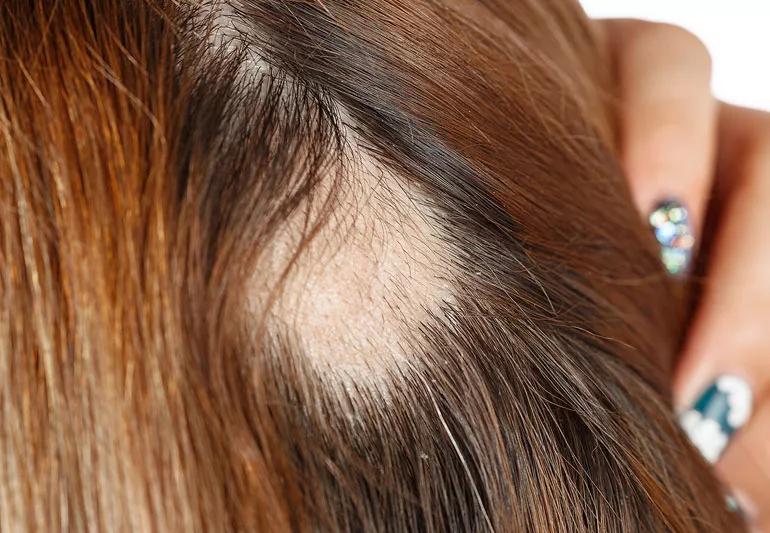
For some, “pulling my hair out” isn’t just an expression — it’s a legit concern. Compulsive hair pulling is a type of body-focused repetitive behavior (BFRB) that affects 1 to 2% of Americans, mostly women. The uncontrollable urge to pull hair can result in bald spots on the scalp, eyebrows and lashes.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Experts don’t know what causes the intense desire to pull hair, but there may be a genetic link. Thankfully, recovery is possible. Preventive medicine physician and wellness expert Sandra Darling, DO, offers some insight.
A: People who compulsively pull their hair often feel shame and embarrassment yet continue pulling anyway because the behavior:
People with a hair-pulling disorder (also known as trichotillomania) may have triggers, like boredom or fatigue. Emotional triggers include feeling anxious, stressed or overwhelmed.
A: People who chronically pull their hair become very good at hiding the behavior if they feel weird or abnormal about it. They may feel like they’re the only person who has this urge, which could lead them to experience emotions such as:
In some cases, the impact of hair pulling goes beyond cosmetic and psychological damage. Some people eat their pulled hairs. The hair can get matted in the digestive tract and create a hairball, which can be life-threatening if it causes a blockage. Surgery may be necessary to remove it.
Advertisement
A: Some people can completely stop hair pulling behavior. For others, trichotillomania is a lifelong disorder that ebbs and flows with life’s events and stressors. Well-meaning friends and family members should avoid telling their loved ones to stop pulling — trichotillomania is a disorder that requires professional help.
If you're caught up in pulling, you can learn to control the urge through a combination of treatments, such as:
A: To hide the condition, many people use hair extensions called crown toppers. They may also use false eyelashes or eyebrow pencils to disguise areas of hair loss. Hats and headscarves are typical as well.
But while you may want to hide the effects, don’t hide the disorder. Be open and honest. Confide in a friend or loved one so you can start on the path to recovery. And you can find inspiration from those who have publicized their struggles with hair pulling, like Megan Fox and JessiKate Riley (Miss Utah 2017).
Advertisement
Learn more about our editorial process.
Advertisement

Fishing for compliments, provoking conflict and pouring on the melodrama are all ways of expressing an unmet need

By setting boundaries around how much you give, you can save your time and resources while also being a good person

Certain B vitamins, omega-3 fatty acids and a healthy diet can serve as complementary treatments for schizophrenia

Following your treatment plan, finding a community, staying active and maintaining a healthy diet can help manage this psychiatric condition

Whether it’s playing hooky or faking cancer, malingering behavior is always motivated by personal gain

Causes range from psychological conditions like PTSD to physical conditions like fibromyalgia

Always putting others’ happiness before your own can build resentment over time

Emotional changes, isolation and unusual behavior could signal the onset of the condition

Start having sex about 72 hours before ovulation, then at least every other day during your fertile window

Attachment theory suggests that your earliest relationships shape connections throughout your life

It isn’t a recognized mental health disorder, but research shows that problematic social media use can negatively affect your mental health, self-esteem and sleep